|
| Formula | Na3KAl4Si4O16 |
| | Optic class & sign | Uniaxial negative |
| | Relief | Low, negative to positive |
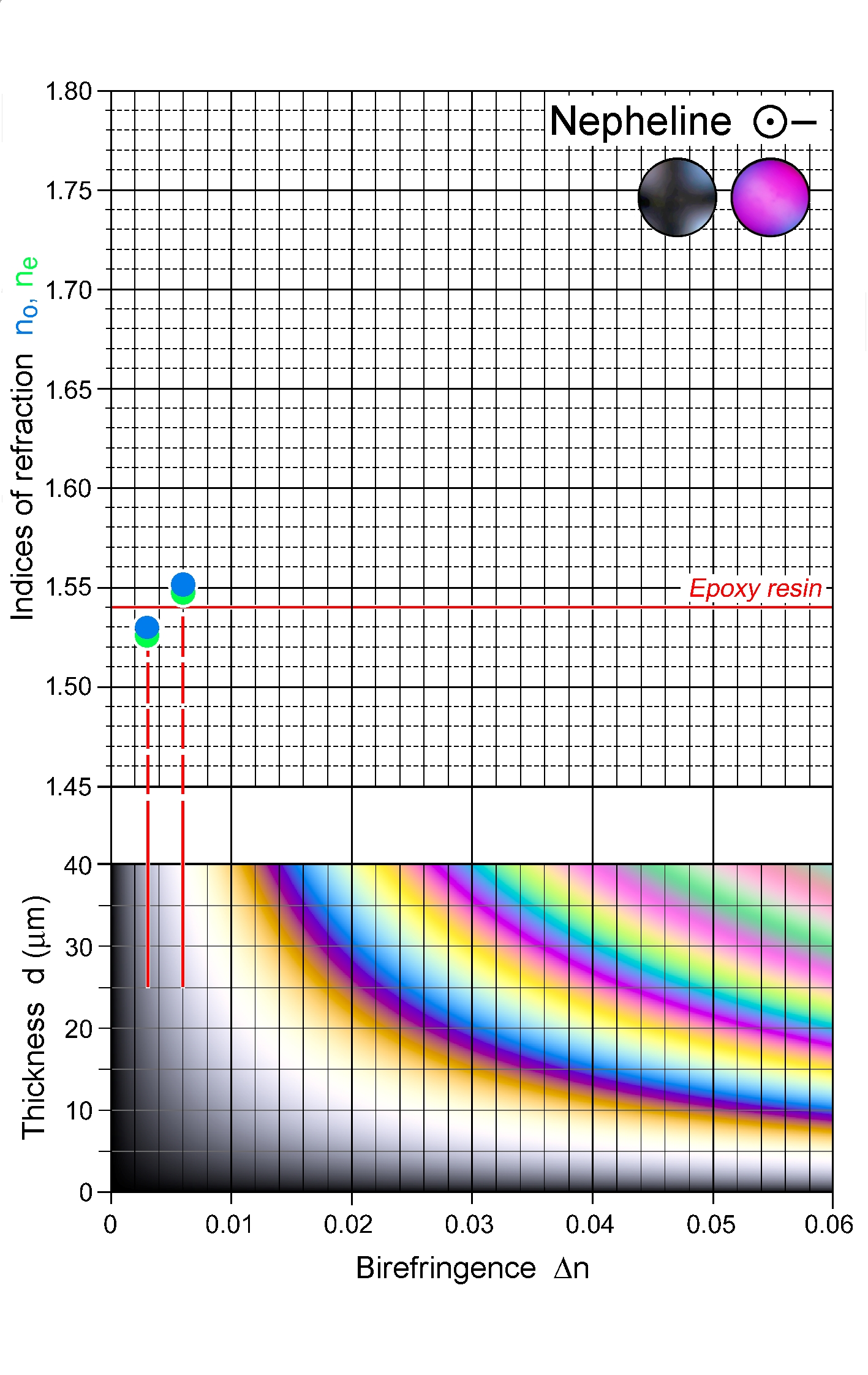
| | Refractive indices | no = 1.529 -1.551
|
|
ne = 1.526 -1.547
|
|
| n increases with increasing K and anorthite component in solid solution, decreases with albite component |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.003 - 0.006 |
| | | - |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-fast, l (-) if crystals are elongate ∥ c; tabular crystals are length-slow, l (+) |
| | Interference figure | Broad, diffuse isogyre cross; low first-order dark to light greys; slight biaxial separation of isogyres may occur |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Short-prismatic to tabular, typically six-sided crystals capped by {0001} basal faces, if euhedral; sections ∥ c are rectangular, basal sections hexagonal |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to subhedral phenocrysts in volcanics (also in groundmass), subhedral to anhedral in plutonic rocks |
| | Cleavage | Basal {0001} and prismatic {1010}, generally poor |
| | Twinning | Commonly not observed |
| | Extinction | Straight to {0001} and {1010} faces in sections ∥ c |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Paragonite, Na-rich zeolites (analcime, natrolite), feldspathoids |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Silica-deficient alkaline rocks, e.g., nepheline syenite, phonolite; also alkalic mafic rocks; basaltic rocks contaminated by carbonate material |
| | | Met | Gneisses and migmatites that experienced alkali metasomatism (nephelinization) |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Low relief and birefringence, form (if euhedral), optic class, lack of twins and cleavage, restriction to silica-poor rocks |
| | Additional comments | Most common feldspathoid mineral; compositional zoning may occur |
|
|

 Images
Images 

 Images
Images 
