|
| Formula | CaMg(CO3)2 |
| | Optic class & sign | Uniaxial negative |
| | Relief | Low negative to high positive; sections with c close to the thin section plane show a marked change of relief over a 90° rotation; strong chagrin in high-relief position (= polarizer parallel to long diagonal of rhomb). |
| | Refractive indices | no = 1.679
|
|
ne = 1.500
|
|
| n and Δn data for endmember composition; n increases with substitution of Fe or Mn for Mg |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.179 |
| | | Δn increases with substitution of Fe or Mn for Mg |
| | Sign of elongation | Hardly applicable due to very high Δn |
| | Interference figure | Well-defined isogyre cross, isochromes over multiple colour orders; rarely anomalous biaxial with small 2V |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Granular, rarely fibrous |
| | | Surface | Anhedral in carbonate aggregates, distributed grains in a matrix may be euhdral; euhedral crystals with curved surfaces in cavities |
| | Cleavage | 3 sets, rhombohedral {1011}, perfect |
| | Twinning | Lamellar on {0221}, 3 sets at 75°, also as deformation twins; simple contact twins on {0001}, {1010}, {1120} |
| | Extinction | Symmetrical to cleavage traces and rhombohedral twin planes in sections subparallel to c. Mottled extinction due to preparation-related, miniscule surface breakouts at cleavage intersections |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Cooling-related unmixing of dolomite as blebs or stringers in high-temperature magnesian calcite |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Soluble, but less so than calcite |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Carbonatites, alkaline dike rocks, rarely in pegmatites |
| | | Met | Pure and impure calcareous-dolomitic metasediments (marble, calcschists, calcsilicate rocks), altered and subsequently metamorphosed ultramafic rocks (e.g., ophicarbonate rocks) |
| | | Sed | Dolomitized carbonate sediments, evaporites |
| | | Hyd | Veins and cavities; gangue mineral in hydrothermal deposits |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | High-order white interference colours, rhombohedral cleavage lamellar twins, and relief change between nO and nE (as for all other rhombohedral carbonates).
Routine optical distinction of the two most common carbonates, calcite and dolomite: Select twinned grains with a distinct change of relief when turning the stage; then select position of max. relief (nO parallel to lower polarizer); the orientation of the twins with respect to O and E directions can now be checked (cf. crystal drawings). In dolomite, the twin lamellae are at a low angle to c (i.e., in thin section the angle to ne' is smaller than 40°). Quantitative distinction of different carbonates in a rock by staining or XRD techniques. |
| | Additional comments | n-Δn chart: Cal - calcite, Dol - dolomite, Kut - kutnahorite, Mgs - magnesite, Rds - rhodochrosite, Sid - siderite, Smt - smithsonite |
|
|

 Images
Images 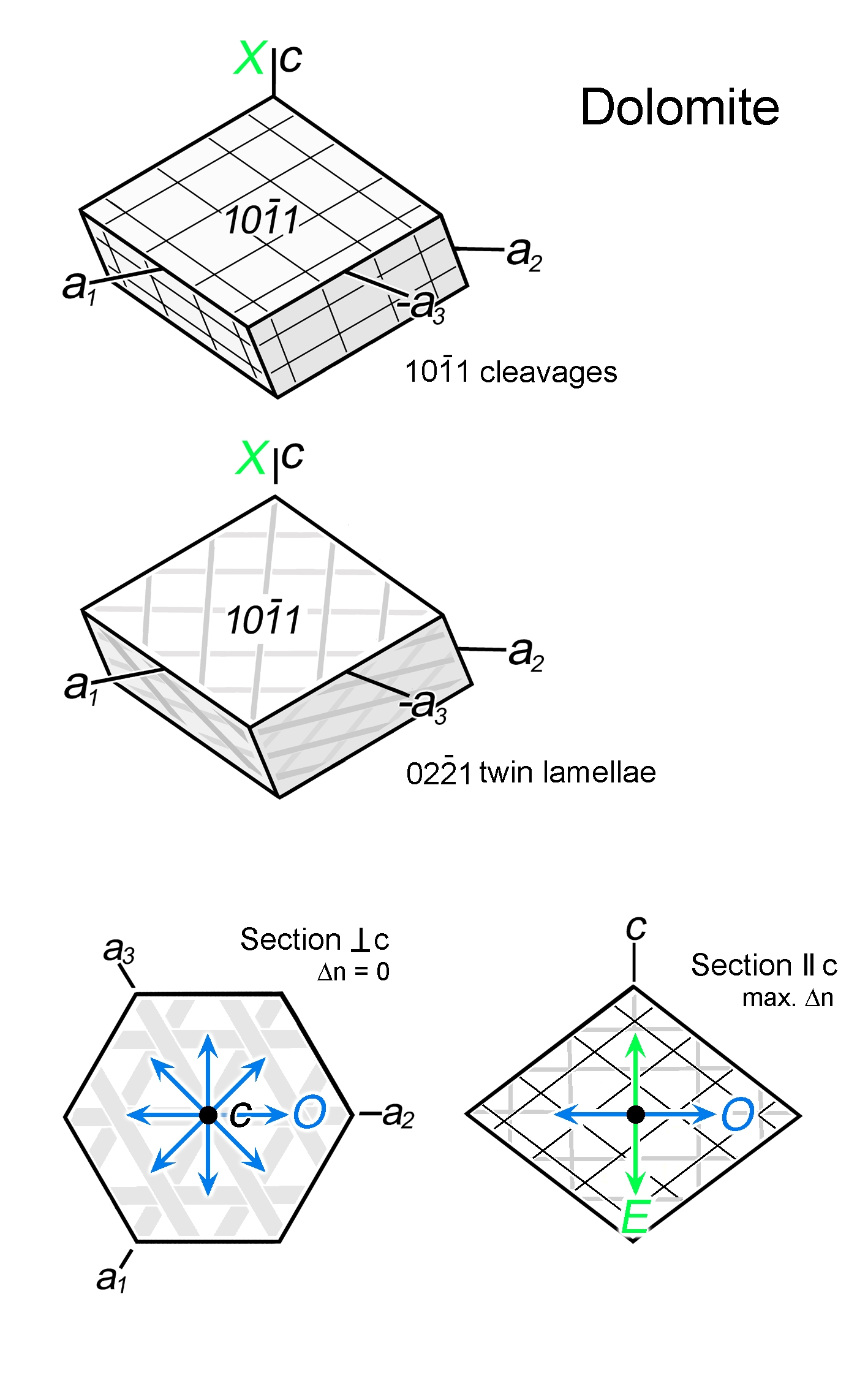


 Images
Images 
