|
| Formula | Ca19(Al,Fe3+)10(Mg,Fe)3(Si2O7)4(SiO4)10(O,OH,F)10 |
| | Optic class & sign | Uniaxial negative |
| | Relief | High |
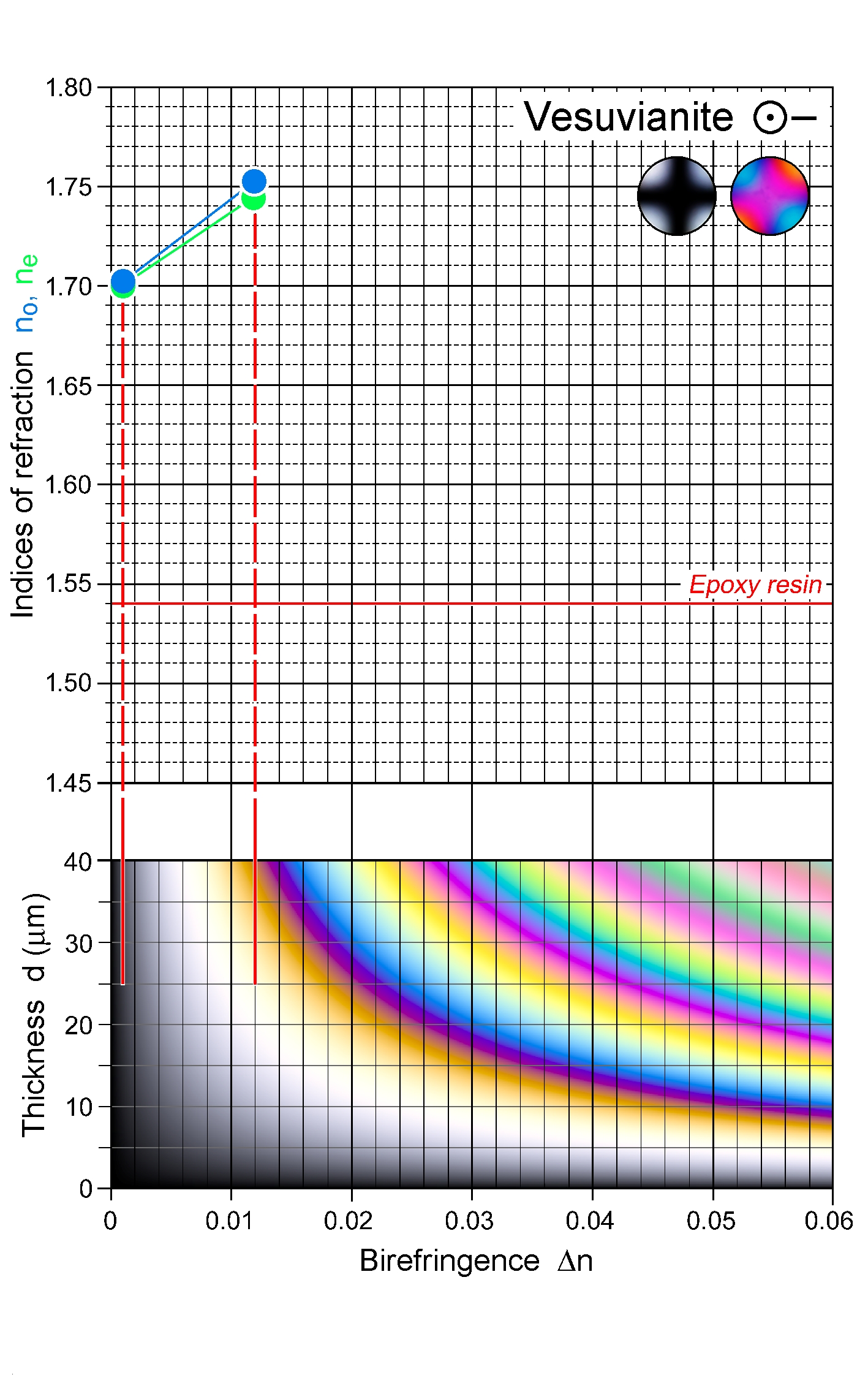
| | Refractive indices | no = 1.702 -1.752
|
|
ne = 1.698 -1.746
|
|
| n increases with increasing Fe2+, Fe3+, or Ti |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.001 - 0.012 |
| | | Anomalous interference colours due to strong dispersion |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-fast, l (-) for crystals elongate in c |
| | Interference figure | Broad isogyre cross, particularly for lower-birefringent varieties; positive optic sign has also been observed in OH-rich varieties which may also be biaxial with 2V up to 65°. Near-isotropic vesuvianite does not yield a useful interference figure. |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless, pale green, pale yellow, pale brown; pleochroism is very weak O>E; colour zoning is common |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Granular to elongate-prismatic; prism faces and/or pyramid faces dominate euhedral crystals; clusters in radial or columnar arrangement, also fibrous |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral |
| | Cleavage | {110}, {100}, {001} poor |
| | Twinning | |
| | Extinction | Straight extinction with respect to prism faces in sections ∥ c; symmetrical to pyramid faces |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Relatively stable |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Nepheline syenite, granite pegmatite |
| | | Met | Impure marble, skarn, calcsilicate rocks, rodingite; restricted to environments with H2O-rich fluid compositions |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | Veins and cavities in hydrothermally altered mafic and ultramafic rocks |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | High relief, very low birefringence, anomalous interference colours, crystal symmetry |
| | Additional comments | Vesuvianite may not generally show strong dispersion, in which case normal first-order interference colours are displayed. |
|
|

 Images
Images 

 Images
Images 
