|
| Formula | (Mg,Fe,Mn,Zn)(Al,Fe3+,Cr)2O4 |
| | Optic class & sign | Isotropic |
| | Relief | High to very high |
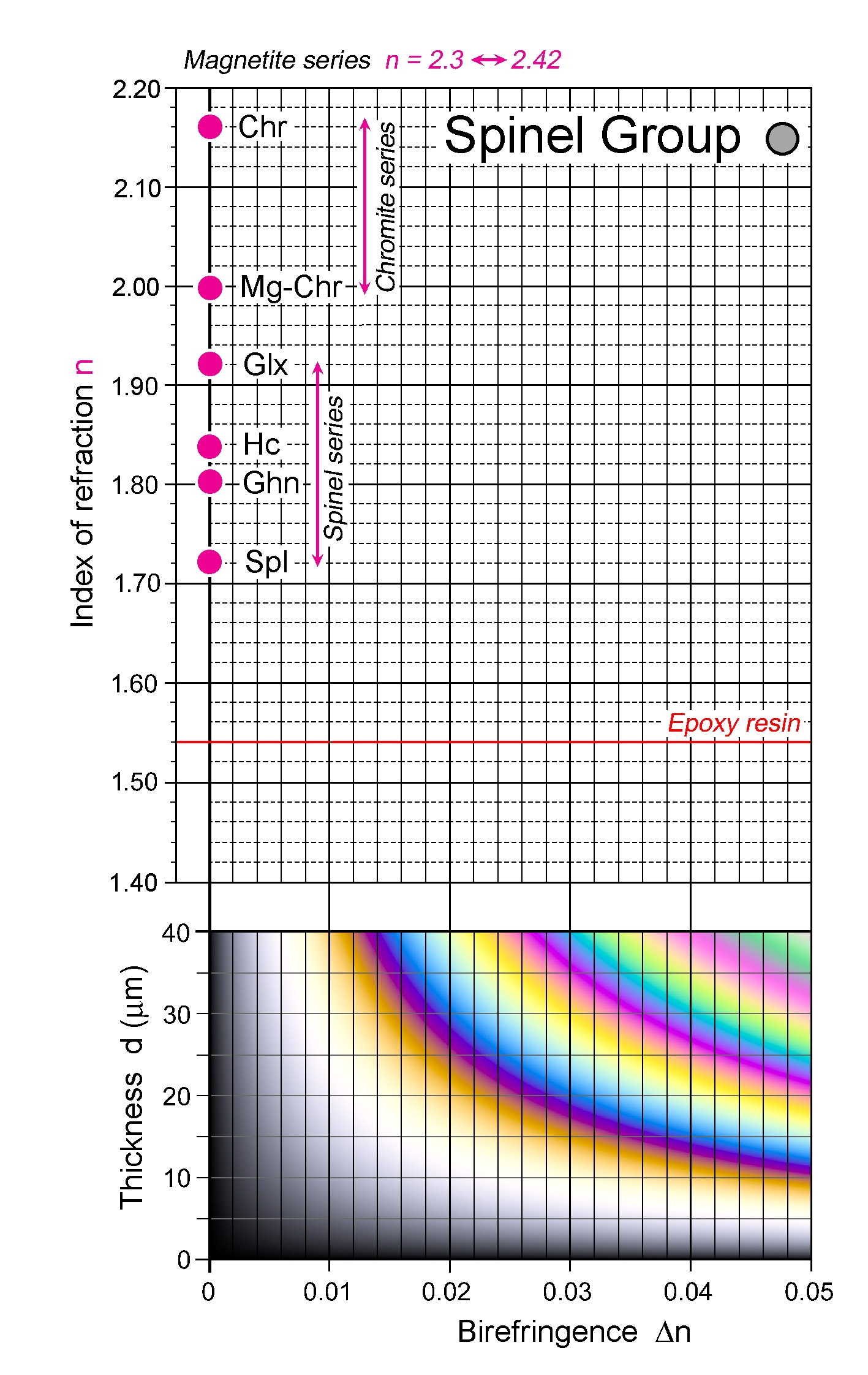
| | Refractive Index | 1.719
-2.05
|
|
| Mg-Fe-Al-dominated spinels 1.719 - 2.05 (spinel-pleonaste-hercynite series, picotite); spinel endmember 1.719, hercynite endmember 1.835; gahnite 1.805, galaxite 1.920; substitution of Fe3+ and Cr for Al increases n
|
| | Birefringence | Zero; weak anomalous birefringence observed in gahnite
|
| | Colour | Highly variable in colour tone and intensity: colourless (Mg-spinel) or weakly to strongly coloured in green, brown, blue, red, yellow; hercynite is dark green; Cr-rich spinels are brown; Fe-, Mn- or Cr-rich spinels may be near-opaque in standard-thickness thin sections
|
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Equant; octahedra if euhedral
|
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral
|
| | Cleavage | None; parting on {111} may occur
|
| | Twinning | Common on {111}, simple or multiple ("spinel law"); can only be recognised in thin section from characteristic crystal outlines
|
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Relatively stable
|
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Mg-Fe-Cr spinel in peridotite, alkremite, mafic rocks and magnetite seams of mafic intrusions,; gahnite in granitic pegmatite and VMS deposits
|
| | | Met | Mg-rich spinel in impure marble, silica-undersaturated calcsilicate and metapelitic rocks; hercynitic spinel in medium- to high-grade aluminous metapelites (hercynite + quartz only in granulite facies), also in metabasites; gahnite in skarns, metamorphosed massive sulphide ores, Zn-bearing metapelites and metabasites; galaxite in Mn-rich metamorphic rocks |
| | | Sed | Detrital in sands (heavy mineral fraction) |
| | | Hyd | Gahnite in metasomatic veins; galaxite in Mn-rich vein deposits
|
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | High n, isotropic, typically intense colour (except Mg-spinel), crystal habit
|
| | Additional comments | Note: The magnetite and chromite series of the spinel group are not considered in the descriptions above |
|
|

 Images
Images 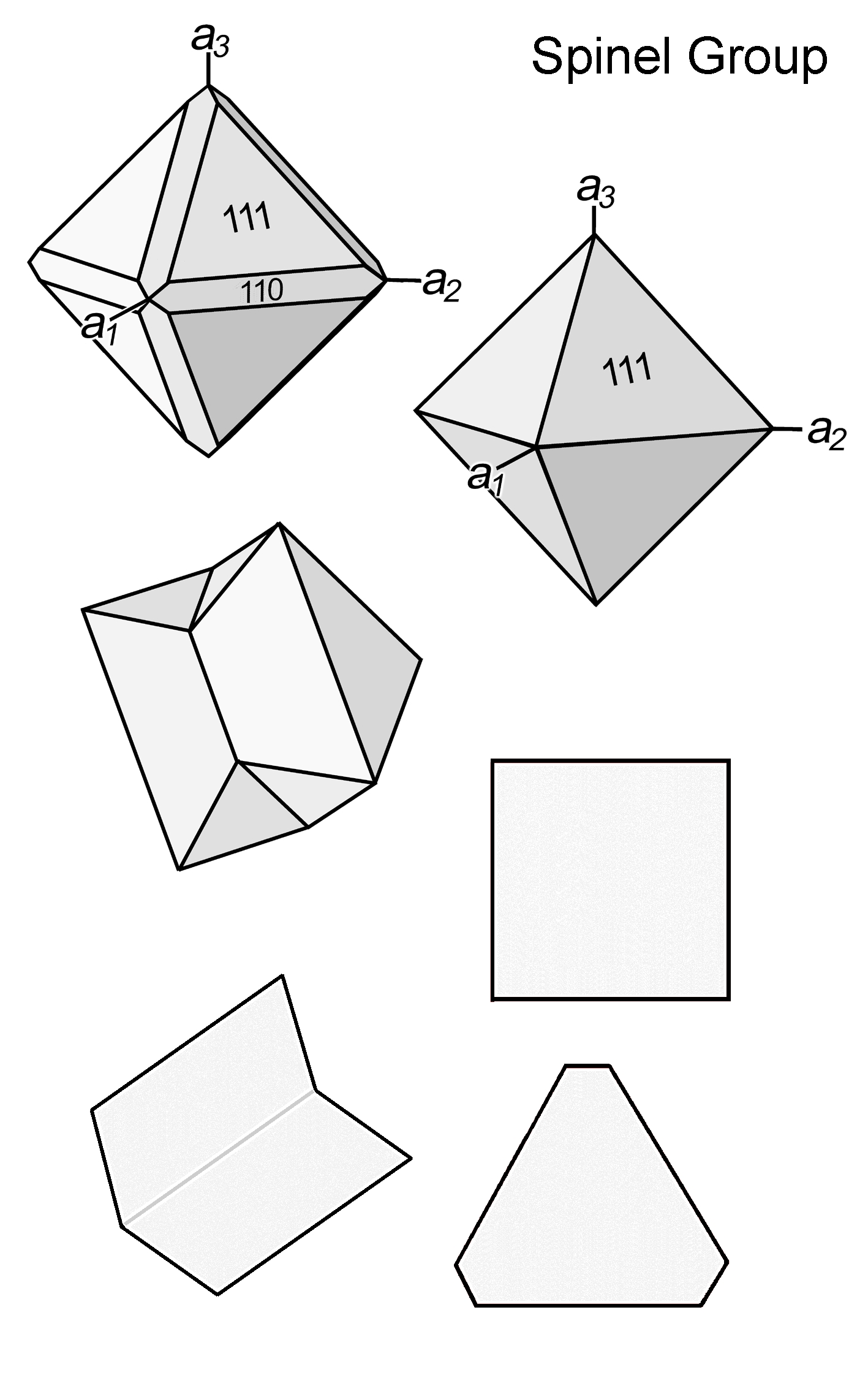

 Images
Images 
