|
| Formula | Fe2O3 |
| | Optic class & sign | Uniaxial negative |
| | Relief | Extreme |
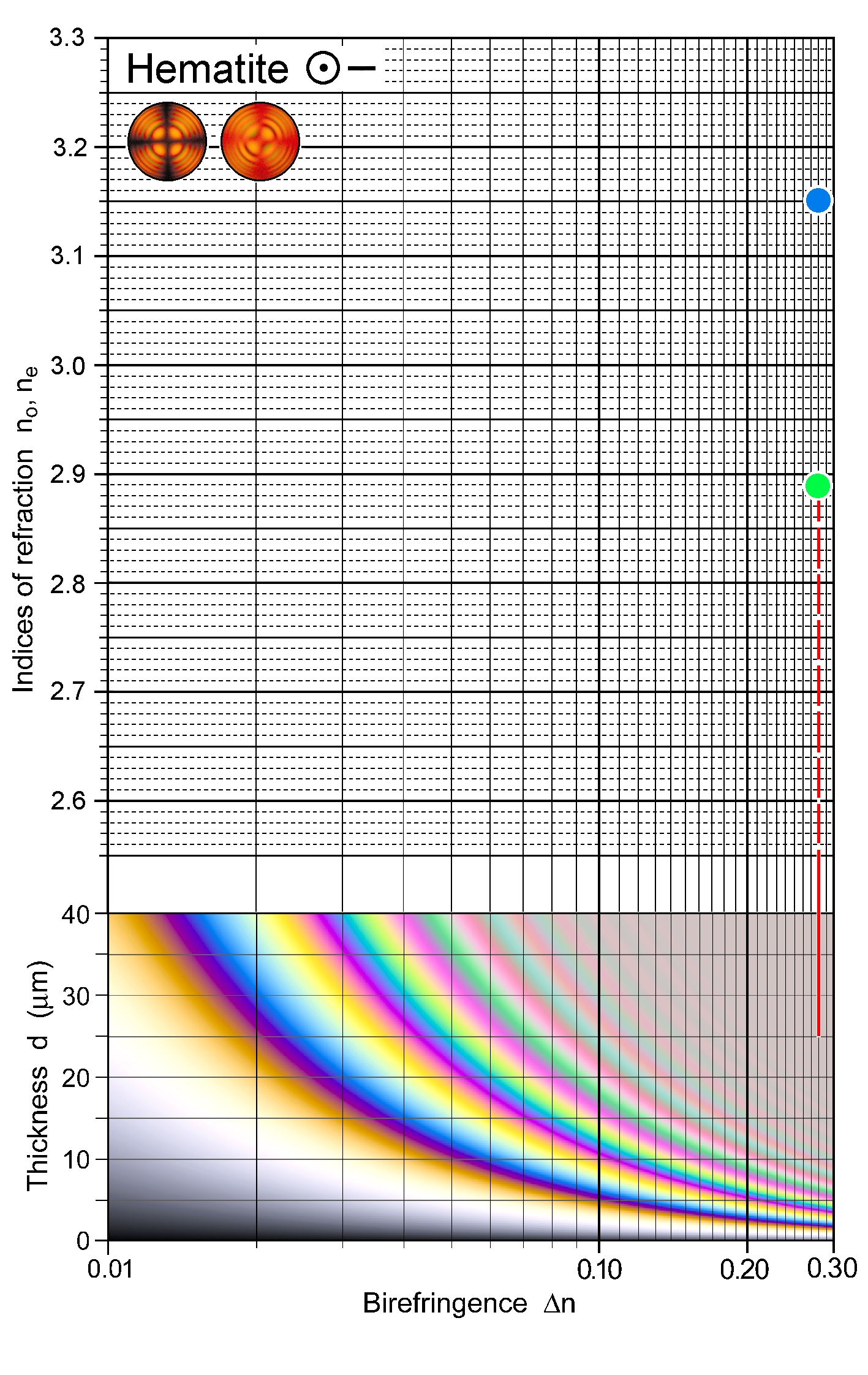
| | Refractive indices | no = 3.15 -3.22
|
|
ne = 2.87 -2.94
|
|
| - |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.28 |
| | | High-order white interference colours, completely masked by mineral colour |
| | Sign of elongation | Not applicable due to colour and extreme Δn |
| | Interference figure | Commonly not obtainable |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Usually opaque; thin crystals (specularite") and crystal edges show deep red-brown colour; pleochroic O>E |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Highly variable; pseudo-hexagonal platelets, trigonal-platy crystals, granular, also in anhedral aggregates; fibrous-radiating aggegates |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral |
| | Cleavage | None; twinning-related parting on basal or rhombohedral planes |
| | Twinning | Lamellar twins, commonly not visible due to grains being opaque |
| | Extinction | Not applicable due to extreme dispersion |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Relatively stable; alteration product of Fe minerals |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Accessory mineral in felsic rocks from oxidised magmas |
| | | Met | Metasedimentary rocks with sufficient Fe3+ |
| | | Sed | Banded ironstones; common mineral in oxidised clastic sedimentary rocks ("red beds") |
| | | Hyd | Surface stains; hydrothermal deposits |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Transmitted light: intense red colour where thin, otherwise opaque |
| | Additional comments | |
|
|

 Images
Images 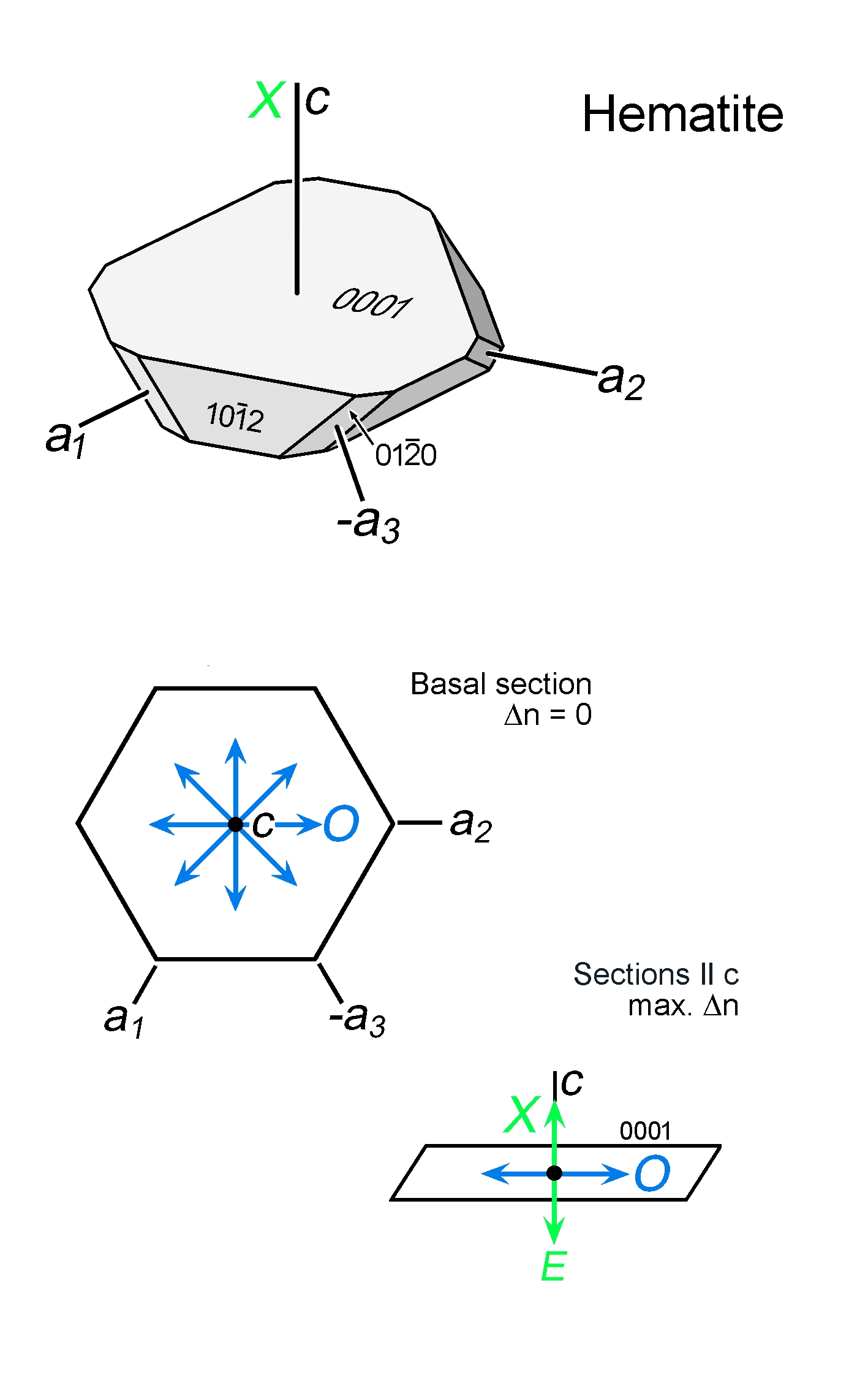

 Images
Images 
