|
| Formula | (Mg,Fe,Mn,Ca)3(Al,Fe3+,Cr)2Si3O12 |
| | Optic class & sign | Isotropic |
| | Relief | High to very high |
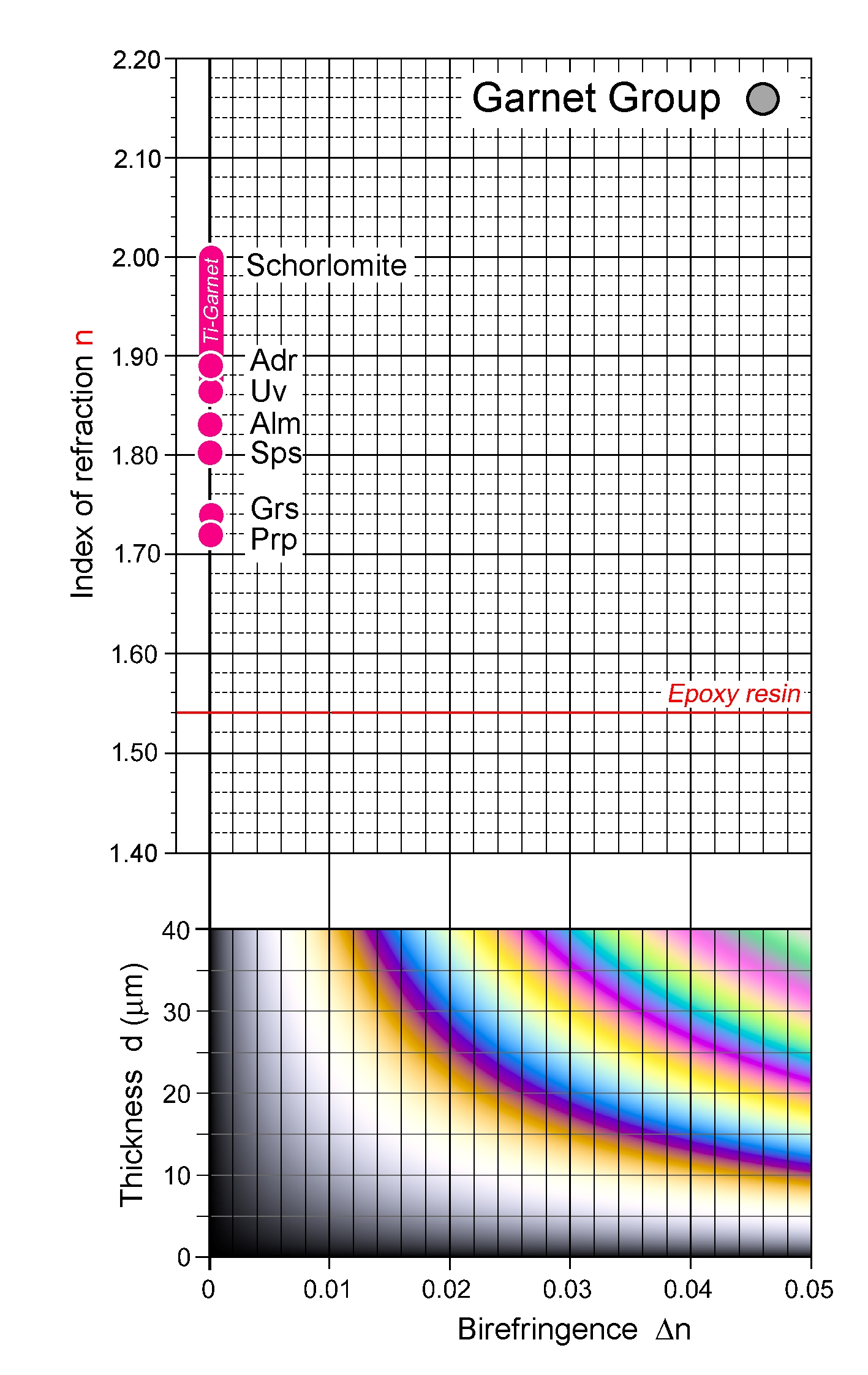
| | Refractive Index | 1.714 -2.00
|
|
| Common quaternary Mg-Fe-Mn-Ca-Al garnets 1.72 – 1.83; Ti-rich garnets (melanite, schorlomite) 1.86 – 2.00; endmembers: pyrope 1.714, almandine 1.830, spessartine 1.800, grossular 1.734, andradite 1.887, uvarovite 1.865 |
| | Birefringence | Zero; anomalous low birefringence up to 0.005 in grossular, andradite, spessartine and uvarovite, particularly in large crystals; concentric zones of variable Δn reflecting compositional zoning may be visible in low-birefringent garnets |
| | Colour | Highly variable; commonly colourless (grossular, near-endmember pyrope) to weakly coloured; pale pink-red, purple, brown, yellow or green; Ti-rich garnets are more intensely yellow-brown; colour zoning reflecting compositional variation may be present |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Commonly equant; particularly where numerous crystal faces are developed, crystals display near-spherical shapes; dodecahedral {110} and/or trapezohedral {112} faces are most common; also irregular forms and skeletal growth |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral; high-positioned in crystalloblastic series; hence the tendency to develop crystal faces against adjacent phases |
| | Cleavage | None; fractures are common; parting on {110} may be present |
| | Twinning | Common, but practically unrecognizable in thin section if mineral is isotropic; wedge-shaped sector twins can be observed in birefringent grains, less commonly lamellar twins on {111} |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Relatively stable at surface conditions; most common alteration product is chlorite |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Garnet peridotite, garnet pyroxenite, megacrysts in kimberlite; granite (S-type in particular), rhyolite, aplite, pegmatite; andradite, melanite and schorlomite in alkaline rocks |
| | | Met | Fe- and/or Mg-dominated aluminous garnets (with variable Mn and Ca contents): metapelites from mid-greenschist to granulite facies incl migmatite (garnet being a common peritectic phase in leucosomes) and restite; blueschist-, eclogite-facies and ultrahigh-pressure metapelites; amphibolite, mafic granulite; blueschist, eclogite; felsic granulite, meta-ironstones; spessartine in Mn-rich skarn and Mn-rich metasediments such as coticules, grossular in impure marble, calcsilicate rocks, skarn, rodingite; andradite in skarn, calcsilicate rocks, low-grade metabasites, serpentinite; Ti-rich garnets also in skarn; uvarovite in Cr-rich serpentinite, calcareous rocks and skarn |
| | | Sed | Detrital in sands (heavy mineral fraction) |
| | | Hyd | Grossular and andradite in hydrothermal veins |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Isotropic, high relief, habit if euhedral, pale colour |
| | Additional comments | Tends to form porphyroblasts in schists and gneisses; can be inclusion-rich and often preserves pre-existing foliations as inclusion trails; garnets with inclusion-rich cores and inclusion-poor rims are common |
|
|

 Images
Images 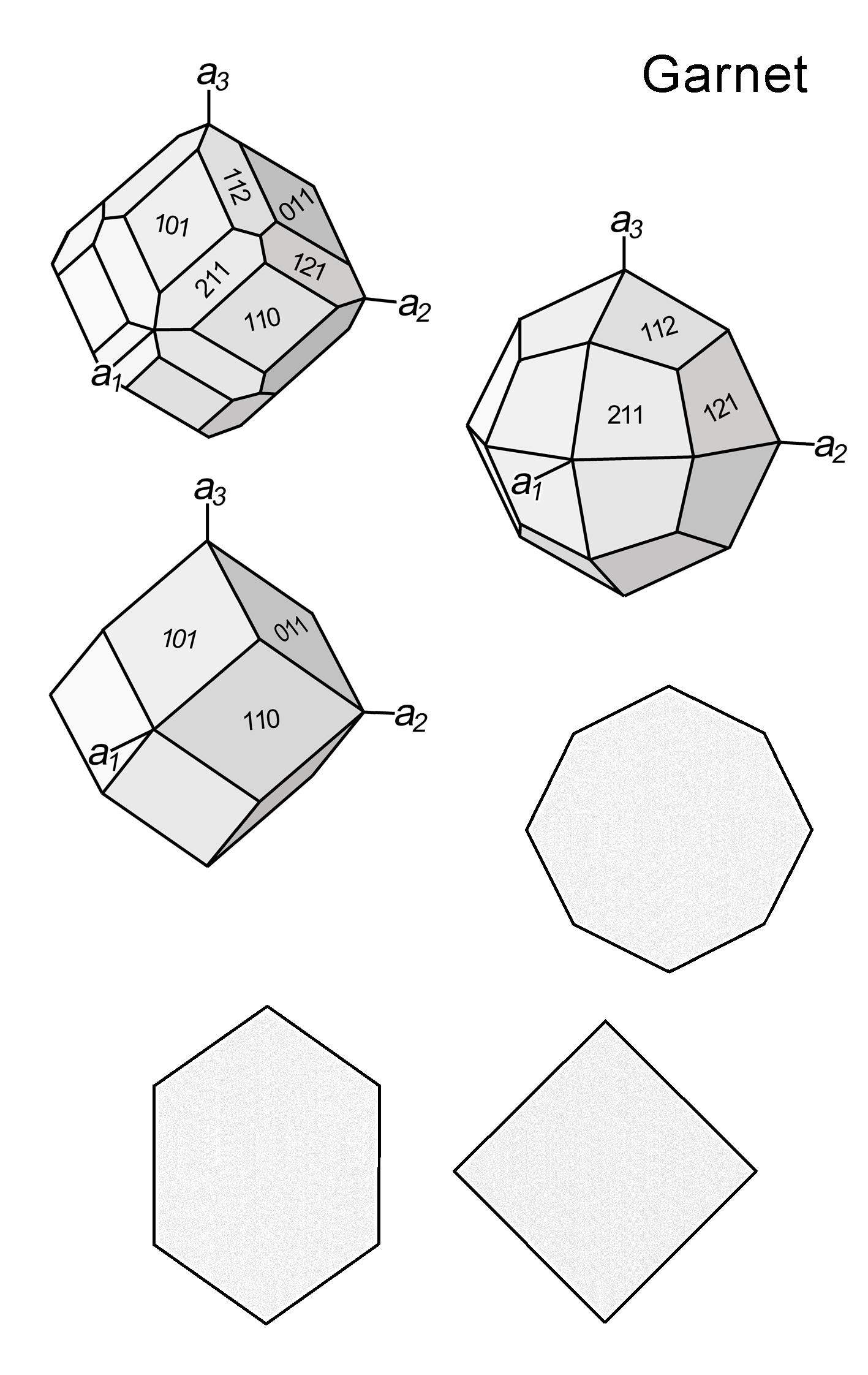

 Images
Images 
