|
| Formula | KAlSi2O6 |
| | Optic class & sign | Isotropic |
| | Relief | Low, negative |
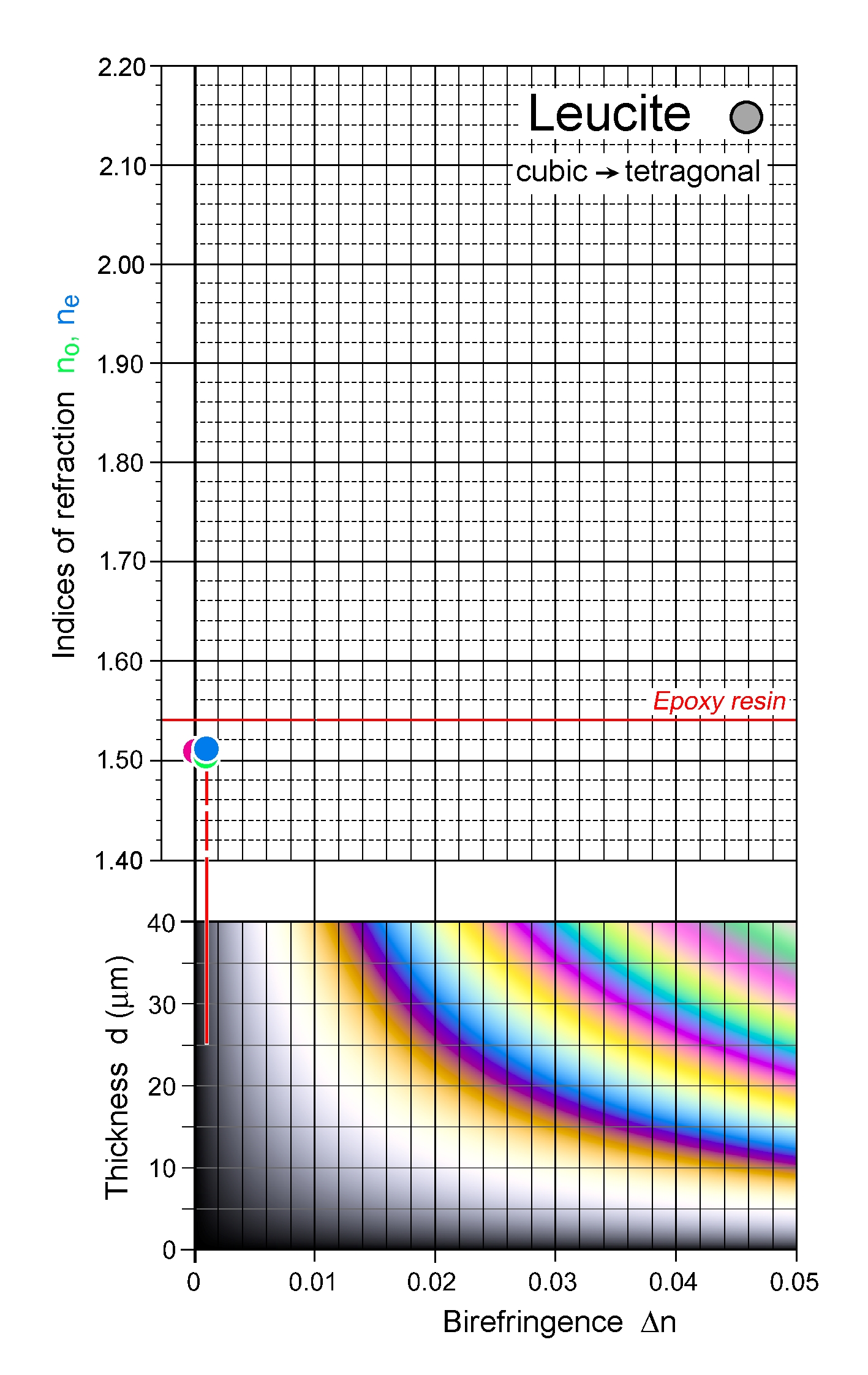
| | Refractive Index | 1.508 -1.511
|
|
| In the low-temperature tetragonal form, the no and ne ranges are approx identical |
| | Birefringence | Zero; tetragonal leucite is still essentially isotropic (Δn = 0.000 - 0.001) |
| | Colour | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Granular; isometric forms: typical are trapezohedra {112}, more rarely dodecahedra {110} |
| | | Surface | Euhedral phenocrysts in volcanics |
| | Cleavage | {110} very poor |
| | Twinning | Intersecting sets of lamellar twins; three sets are typically visible, intersecting at about 60°, and resulting from transformation of the high-temperature cubic structure to the low-temperature tetragonal structure |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Intergrown nepheline and K-feldspar ("pseudoleucite"); analcime, clays; pseudomorphs of alteration products after leucite are more widespread than unaltered material |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Si-Na-poor, potassic volcanic rocks and shallow-level intrusives such as leucite basalt, leucite tephrite, leucite basanite, leucitite |
| | | Met | |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Habit, very low birefringence, characteristic twinning |
| | Additional comments | Transformation of cubic leucite to tetragonal symmetry during cooling (then optically uniaxial positive); radial and concentric patterns of small inclusions may be present; |
|
|

 Images
Images 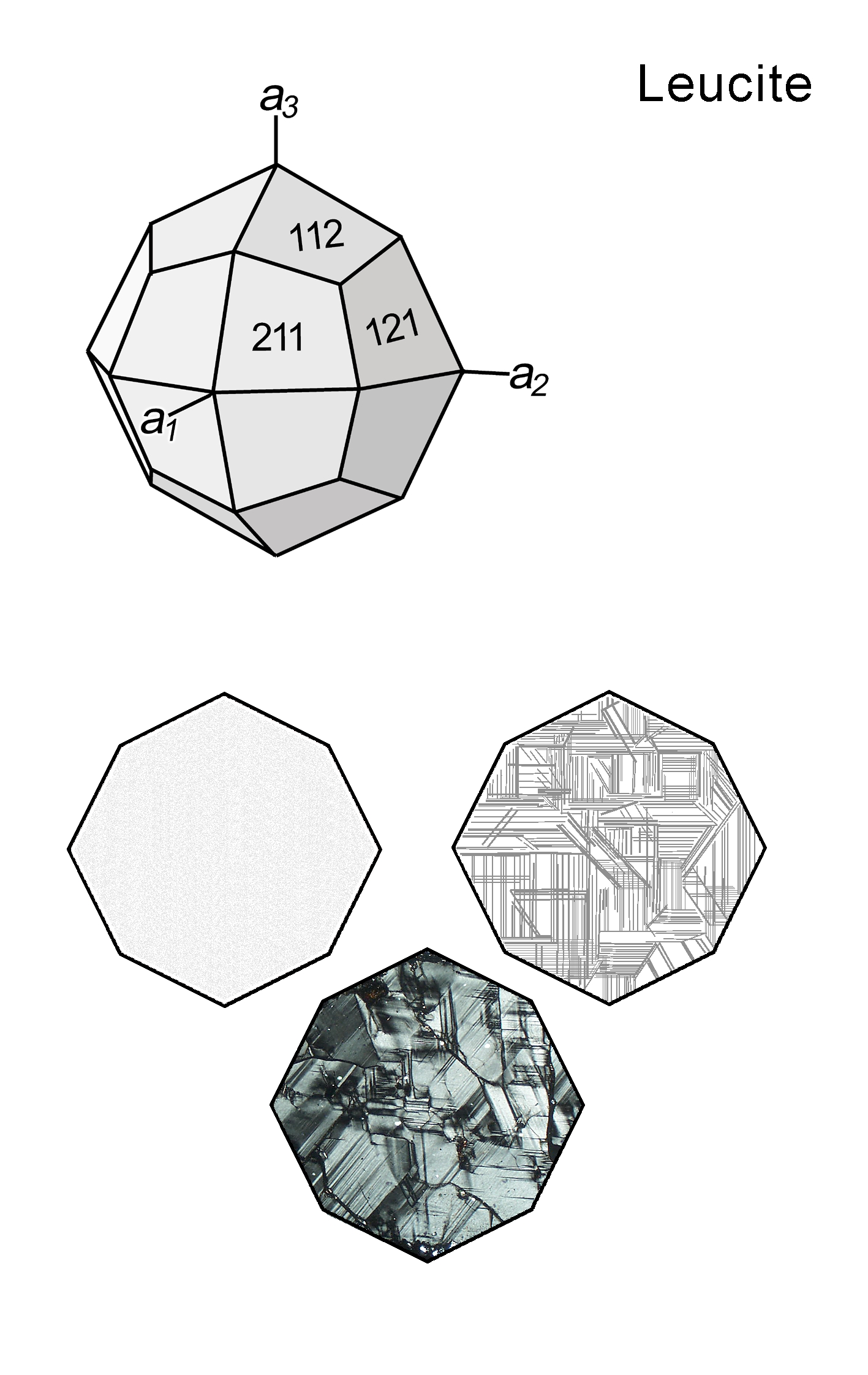

 Images
Images 
