|
| Formula | Al2SiO5 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | a = Z, b = Y, c = X |
| | Optical plane | (010) |
| | Relief | Moderate positive |
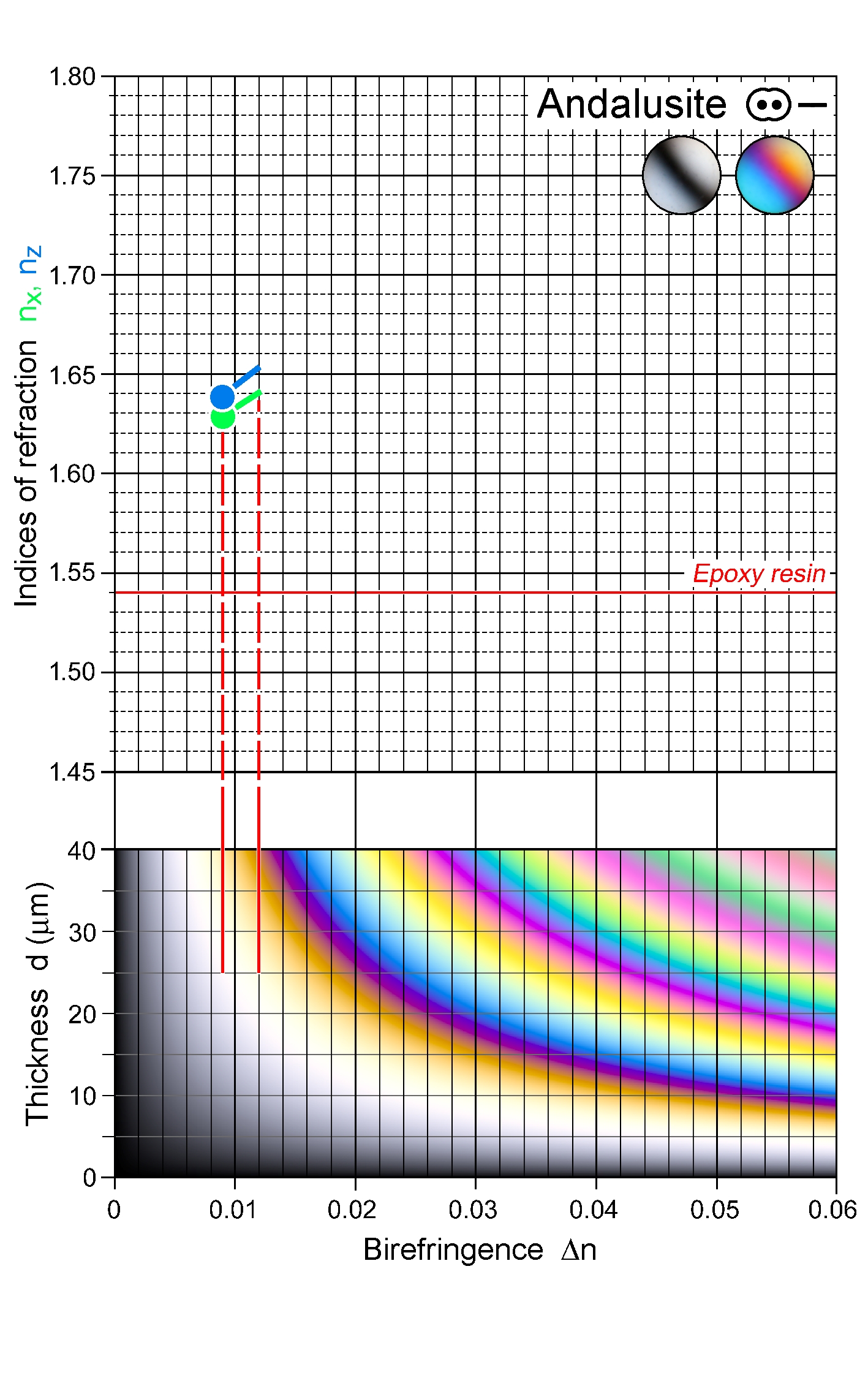
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.629 -1.640
|
|
ny = 1.634 -1.644
|
|
nz = 1.638 -1.650
|
|
| n increases with increasing Fe3+ and Mn3+ |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.009 - 0.012 |
| | | In the andalusite-viridine series Δn decreases from the Al endmember (max Δn) to zero at about 6.5 mol% Mn + Fe, then increasing again where optic sign is positive (see under viridine). |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 71 - 88° |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | Length-fast, l (-) |
| | Interference figure | Acute bisectrix figures from sections ⊥ c with melatopes outside the field of view, due to high 2V |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Commonly colourless; may show pink, yellow or green colour, then pleochroic with X = pink or yellow, Y = Z = colourless, pale yellow or pale green; colour intensity increases towards viridine; chiastolite varieties may have a distinct coloured-pleochroic core zone |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Elongate-prismatic to short-columnar; also irregular forms; square-shaped (pseudotetragonal) sections ⊥ c of euhedral crystals |
| | | Surface | Euhedral crystals are common in graphitic rocks; subhedral to anhedral crystals occur more typically in non-graphitic rocks |
| | Cleavage | 2 sets of {110} prismatic cleavage at nearly 90° |
| | Twinning | Rare on {101} |
| | Extinction | Symmetrical to {110} prism faces and cleavage in basal sections; straight to prism faces and cleavage in sections parallel to c |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Replacement of andalusite by sillimanite or kyanite, resulting from prograde metamorphism or polymetamorphism. Retrograde transformation of sillimanite or kyanite to andalusite is much less common. |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Sericite, kaolinite, pyrophyllite |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Peraluminous granites; rare in pegmatites |
| | | Met | Low-pressure Al-rich pelitic rocks in contact- and (low-pressure) regional-metamorphic environments |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | May occur in quartz veins |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Relief, low Δn, extinction characteristics, l (-), pseudo-tetragonal form if euhedral, association with other Al-silicates
The chiastolite variety shows a unique and characteristic inclusion pattern mainly along the diagonals of the pseudo-tetragonal prism, forming a feathery cross in sections orthogonal to c. Accumulation of graphite on prism faces can be observed in carbonaceous rocks.
|
| | Additional comments | In schists, andalusite tends to form inclusion-rich porphyroblasts. |
|
|

 Images
Images 

 Images
Images 
