|
| Formula | Al2SiO5 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | a near X, b near Y, c near Z |
| | Optical plane | Subparallel to a and inclined about 30° to both b and c |
| | Relief | High |
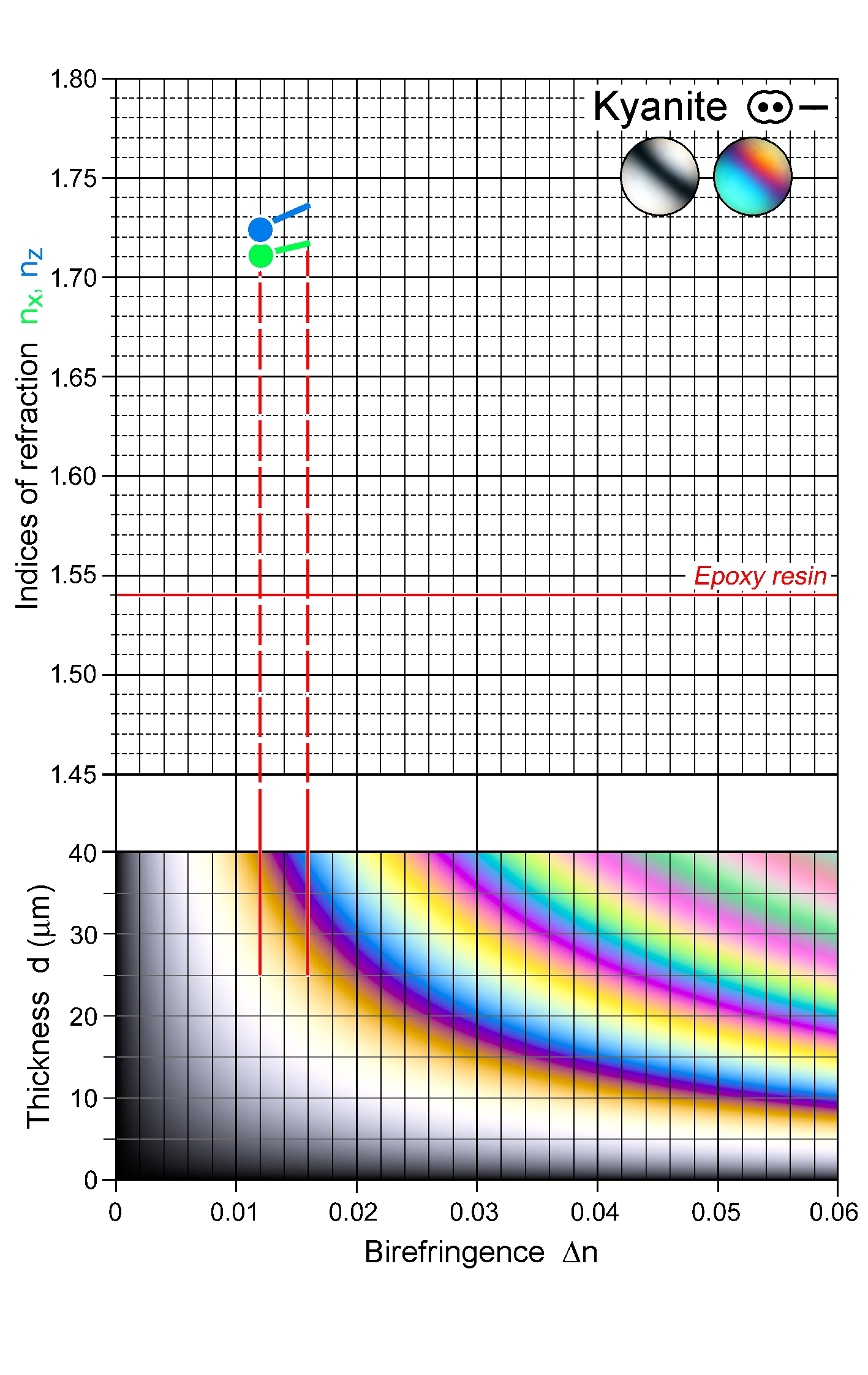
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.710 -1.718
|
|
ny = 1.719 -1.724
|
|
nz = 1.724 -1.734
|
|
| - |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.012 - 0.016 |
| | | - |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 78 - 84° |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+) |
| | Interference figure | {100} sections yield acute bisectrix figures with melatopes well outside the field of view. Few isochromatic rings in optic axis figures |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Commonly colourless, also pale blue and pleochroic with absorption Z > Y > X, whereby X = colourless, Y = light violet-blue, Z = light cobalt blue; colour distribution may be patchy |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Bladed, columnar, also acicular |
| | | Surface | Typically subhedral to euhedral |
| | Cleavage | {100} perfect, {010} distinct; parting on {001} |
| | Twinning | Simple or multiple twinning on {100} common, multiple twins on {001} less common |
| | Extinction | Max extinction angle 30° for {100} sections; sections orthogonal to {100} show near-parallel extinction |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Replacement of andalusite by kyanite resulting from presssure increase during metamorphism, or from polymetamorphism |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Sericite, kaolinite, pyrophyllite |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Rare in granite and pegmatites |
| | | Met | Al-rich pelitic rocks from intermediate- or high-pressure environments, eclogites, high-pressure granulites, metabauxites |
| | | Sed | Detrital in sands |
| | | Hyd | May occur in quartz veins |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | High relief, birefringence, characteristic cleavage, twinning |
| | Additional comments | Intermediate- to high-pressure Al2SiO5 polymorph |
|
|

 Images
Images 

 Images
Images 
