|
| Formula | Ca2Al3O(Si2O7)(SiO4)OH |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive |
| | Optical orientation | Zoisite: a = X, b = Y, c = Z; ferrian zoisite: a = Y, b = X, c = Z |
| | Optical plane | Zoisite: (010), ferrian zoisite: (100) |
| | Relief | High |
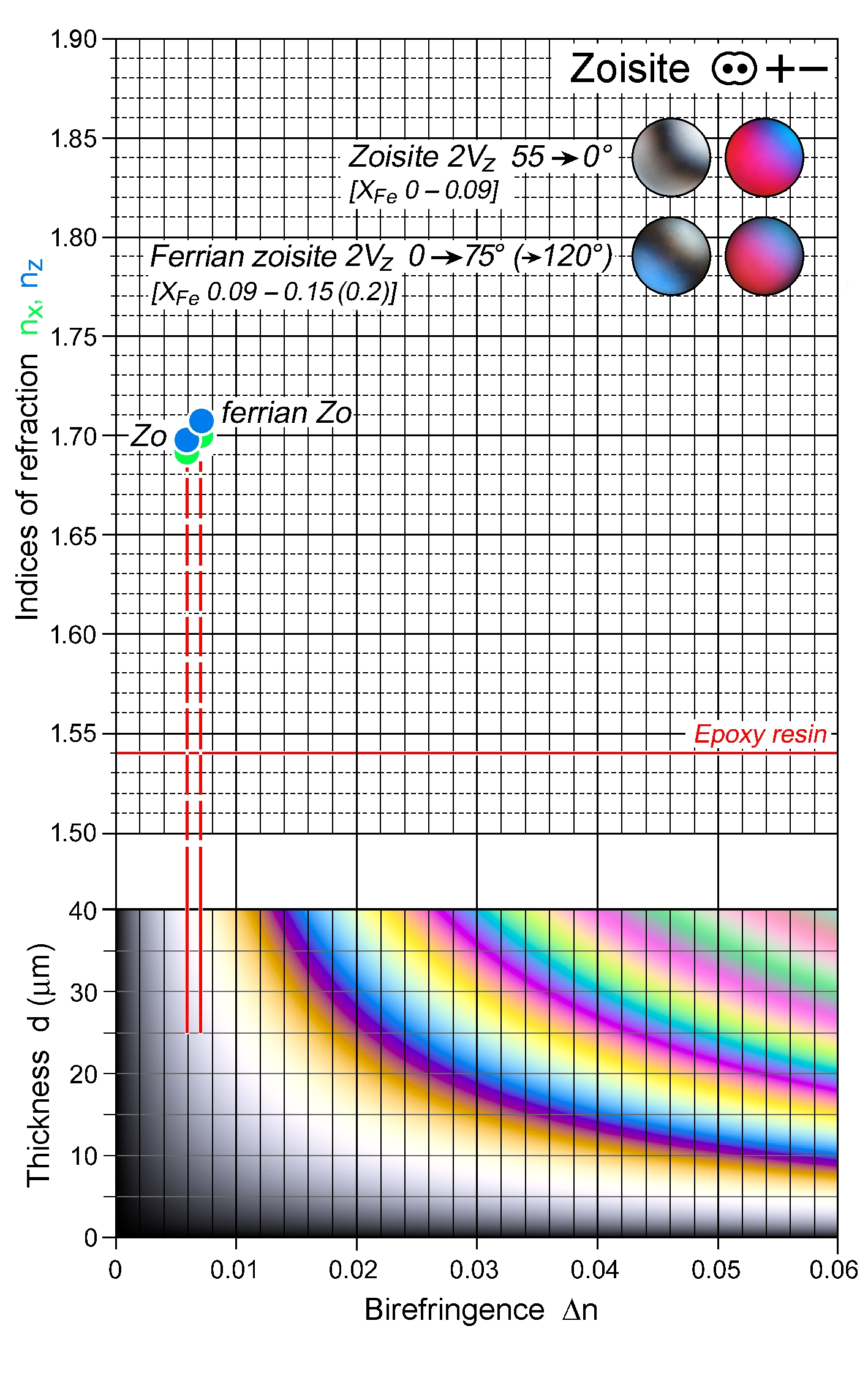
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.690 -1.703
|
|
ny = 1.692 -1.706
|
|
nz = 1.696 -1.710
|
|
| n increases with Fe3+ |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.006 - 0.007 |
| | | Anomalous blue and yellow interference colours due to strong dispersion |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 60 - 90° |
| | 2Vz
= 90 - 0° |
| | Sign of elongation | Zoisite: length-slow and length-fast, l (+) or l (-), for crystals elongate in b = Y; ferrian zoisite: length-fast, l (-) |
| | Interference figure | Highly variable, with 2V = 0° at the transition zoisite / ferrian zoisite; strong optic axis dispersion |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Prismatic crystals, columnar to fibrous, also in aggregates; granular aggregates |
| | | Surface | Anhedral in granular aggregates; prismatic crystals subhedral to euhedral |
| | Cleavage | {010} perfect |
| | Twinning | Not common |
| | Extinction | Straight to prism faces and cleavage in sections ∥ b |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Breakdown product of anorthite |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Relatively resistant in surface environments |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Rare in mafic and ultramafic rocks |
| | | Met | Ca-bearing schists and gneisses; marble; blueschists and eclogite |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | In "saussurite", a polymineralic hydrothermal alteration product of plagioclase |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | High relief, low Δn, anomalous interference colours, straight extinction |
| | Additional comments | Zoisite is the Fe3+-poor variety; as Fe3+ increases to ferrian zoisite , the optical orientation changes; this transition occurs where 2V = 0°, at about 0.09 Fe3+ p.f.u.
The Mn-enriched variety of zoisite is thulite. The refractive index ranges are: nX = 1.690 - 1.703 , nY = 1.693 - 1.705, nZ = 1.700 - 1.725; Δn = 0.008 - 0.022; 2V = 30 -70° (data largely based on Schaller & Glass 1942, Am. Min. 27, 519-524). Colour and pleochroism: X = pink, Y = pale pink or colourless, Z = pale yellow. Higher Mn concentration in the core of grains is common. Mn in Thulite is mainly replacing Ca (as Mn2+) and not Al (by Mn3+) as suggested in older works. The monoclinic variety, clinothulite, has a similar compositional range as thulite. Thulite and clinothulite occur in pegmatites, impure calcitic and dolomitic marble, and in hydrothermal veins. |
|
|

 Images
Images 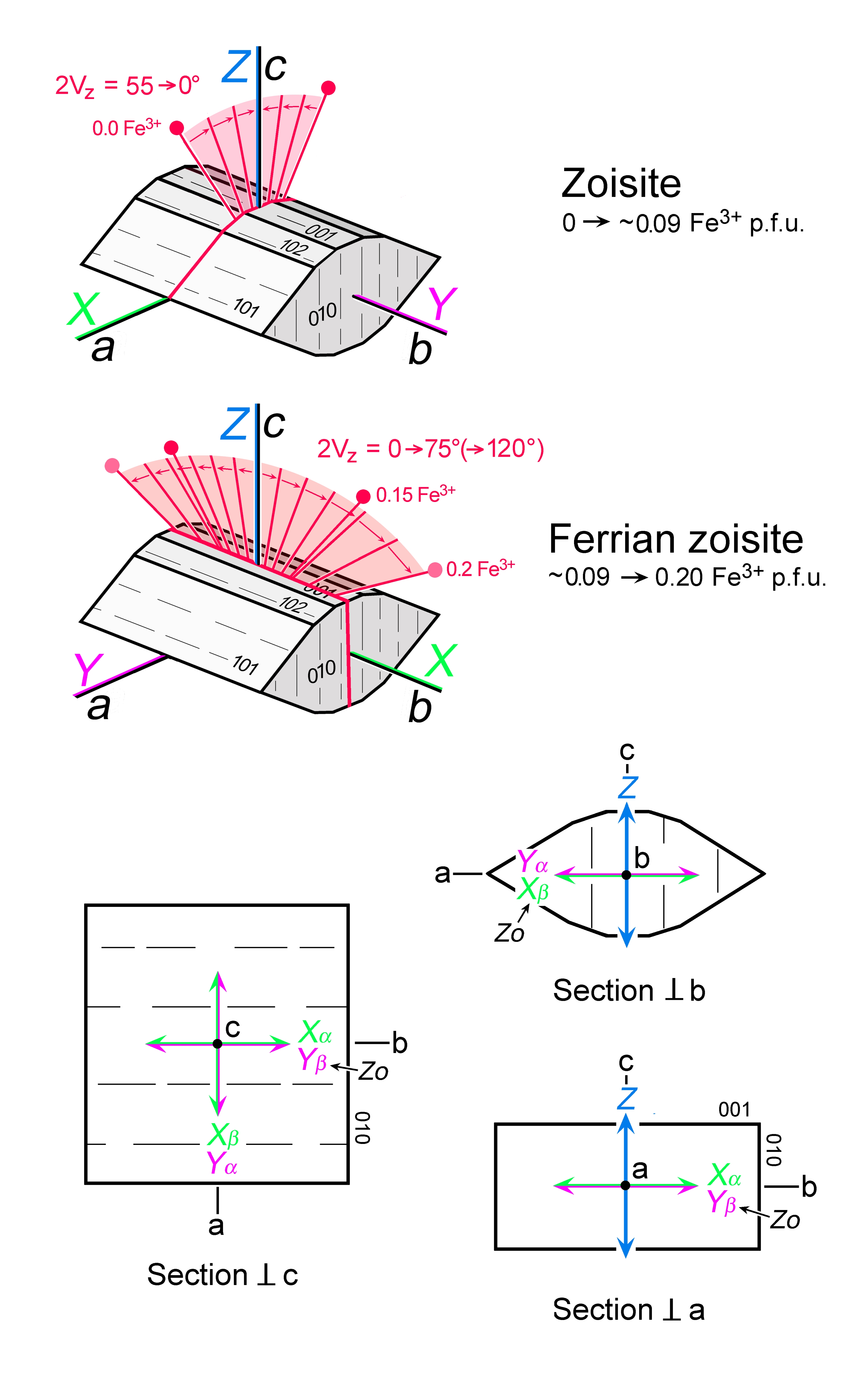

 Images
Images 
