|
| Formula | CaTiSiO4(O,OH,F) |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive |
| | Optical orientation | a near X, b = Y, c Λ Z = 36 - 51° |
| | Optical plane | (010) |
| | Relief | Very high |
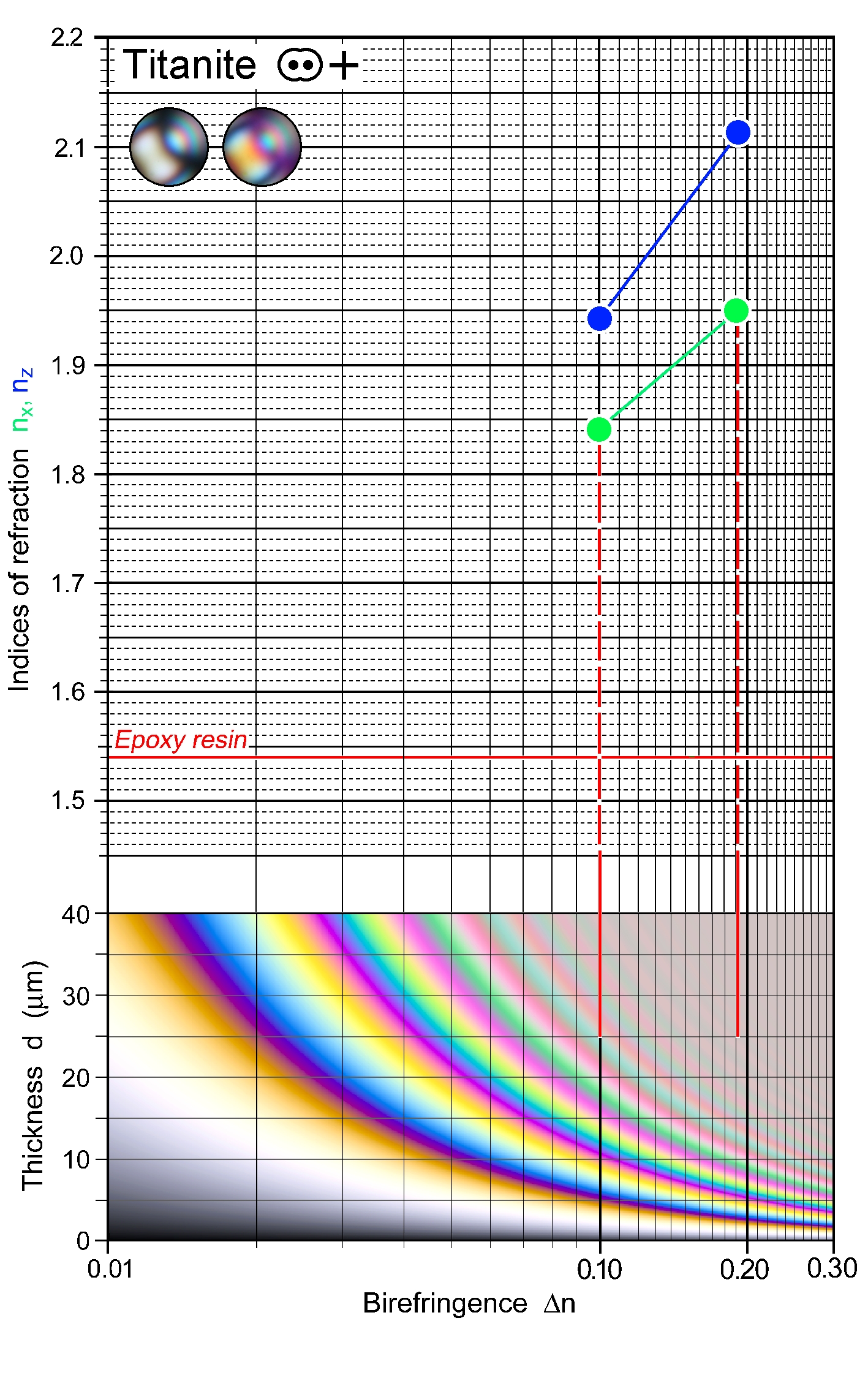
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.843 -1.950
|
|
ny = 1.870 -2.034
|
|
nz = 1.943 -2.110
|
|
| n decreases with replacement of Ti by Al and Fe3+ |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.100 - 0.192 |
| | | Δn decreases with replacement of Ti by Al and Fe3+. Max interference colour is a high-order white, in coloured varieties, the mineral colour blends with the interference colour. Sections near-orthogonal to an optic axis show a display of anomalous interference colours when rotating the stage; an extinction position is not defined with polychromatic light. |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
|
| | 2Vz
= 17 - 40° |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-fast, l (-) for the long diagonal of (010) sections, but determination is impractical due to very high Δn |
| | Interference figure | Due to high Δn, interference figures show numerous isochromatic rings. Strong optic axis dispersion causes colour fringes on isogyres. |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless to various shades of pale brown, then weakly pleochroic Z > Y > X, with X = colourless to pale yellow, Y = pale yellow-brown, pale pink, greenish yellow, Z = grey-brown, pink, orange-brown, greenish brown |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Granular, characteristic rhomb-shaped crystals if euhedral |
| | | Surface | Commonly subhedral to euhedral if isolated crystals |
| | Cleavage | {110}, 2 sets, but normally not obvious in thin section |
| | Twinning | Simple twins {100} with twin plane along the long diagonal of the rhomb; also multiple twins on {221} |
| | Extinction | Mostly inclined to crystal faces; symmetrical in rhomb sections |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Titanite coronas around rutile or ilmenite may be observed |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Alteration to opaque leucoxene (Ti-oxides, quartz and other minerals). Titanite may form as a product of biotite or Ti-augite alteration. |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Most common in silica-undersaturated and intermediate plutonic rocks (syenite, monzonite, granodiorite, diorite); granite pegmatites; phonolite |
| | | Met | Ca-rich schists and gneisses, amphibolites, marble, calcsilicate rocks, blueschists |
| | | Sed | Detrital in the heavy mineral fraction of sands; also authigenic |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Very high relief and birefringence; characteristic crystal form. Compared to carbonates, the change of relief in max birefringence sections when rotating the stage is far less distinct to the eye. |
| | Additional comments | Where sufficient radiogenic isotopes are contained in titanite, α-radiation damage creates pleochroic halos in some ferro-magnesian host minerals. |
|
|

 Images
Images 

 Images
Images 
