|
| Formula | CaSO4 ∙ 2H2O |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive |
| | Optical orientation | X near a, Y = b, Z at a high angle to c (52°) |
| | Optical plane | (010) |
| | Relief | Low-negative |
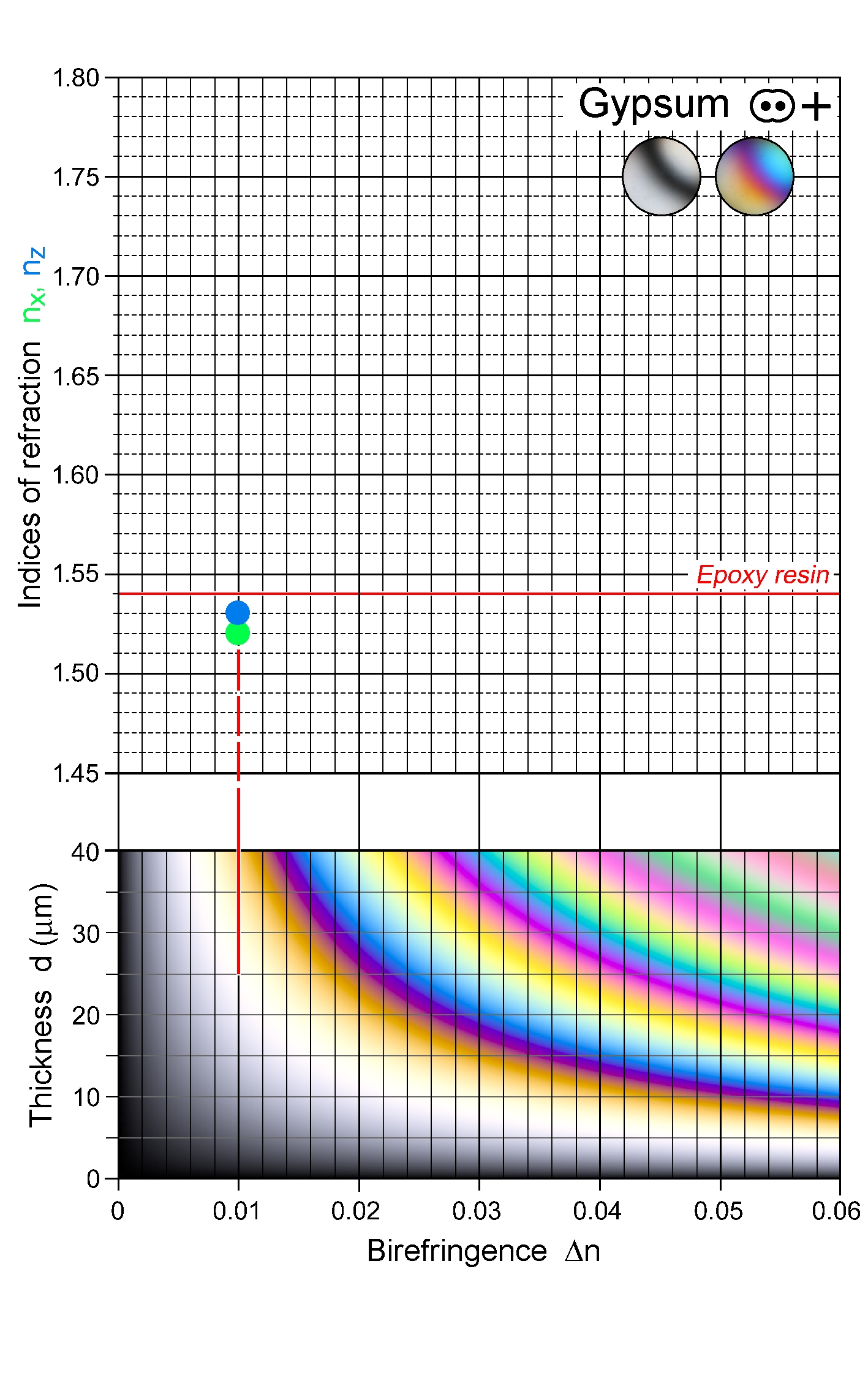
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.519 -1.521
|
|
ny = 1.522 -1.526
|
|
nz = 1.529 -1.531
|
|
| - |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.009 - 0.010 |
| | | - |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
|
| | 2Vz
= 58° - |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+), or length-fast, l (-), in sections at a high angle to (010); in prismatic sections, the sign of elongation is problematic to determine, due to the large ZɅc angle. |
| | Interference figure | Broad and diffuse isogyres on a mid-first-order white background |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Tabular, elongate-prismatic or acicular ∥ c, rarely ∥ a, rosettes, granular; crystals may be curved |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral |
| | Cleavage | {010} perfect, {100} distinct, 2 sets {111} good, intersecting at 42° and 138° |
| | Twinning | Simple {100} |
| | Extinction | Generally oblique; max extinction angles ZɅc and XɅc in (010) sections; sections ∥ b show straight extinction to traces of (010) cleavage and (010) crystal faces. |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Gypsum is itself a hydration product of anhydrite and also a weathering product of sulfides |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | |
| | | Sed | Evaporite deposits; secondary from hydration of anhydrite; speleothems; efflorescent in desert sand (“desert roses”) |
| | | Hyd | Oxidized zone of sulfide deposits; precipitate around fumaroles and volcanic vents |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Low birefringence, low negative relief, characteristic cleavages, inclined extinction |
| | Additional comments | |
|
|

 Images
Images 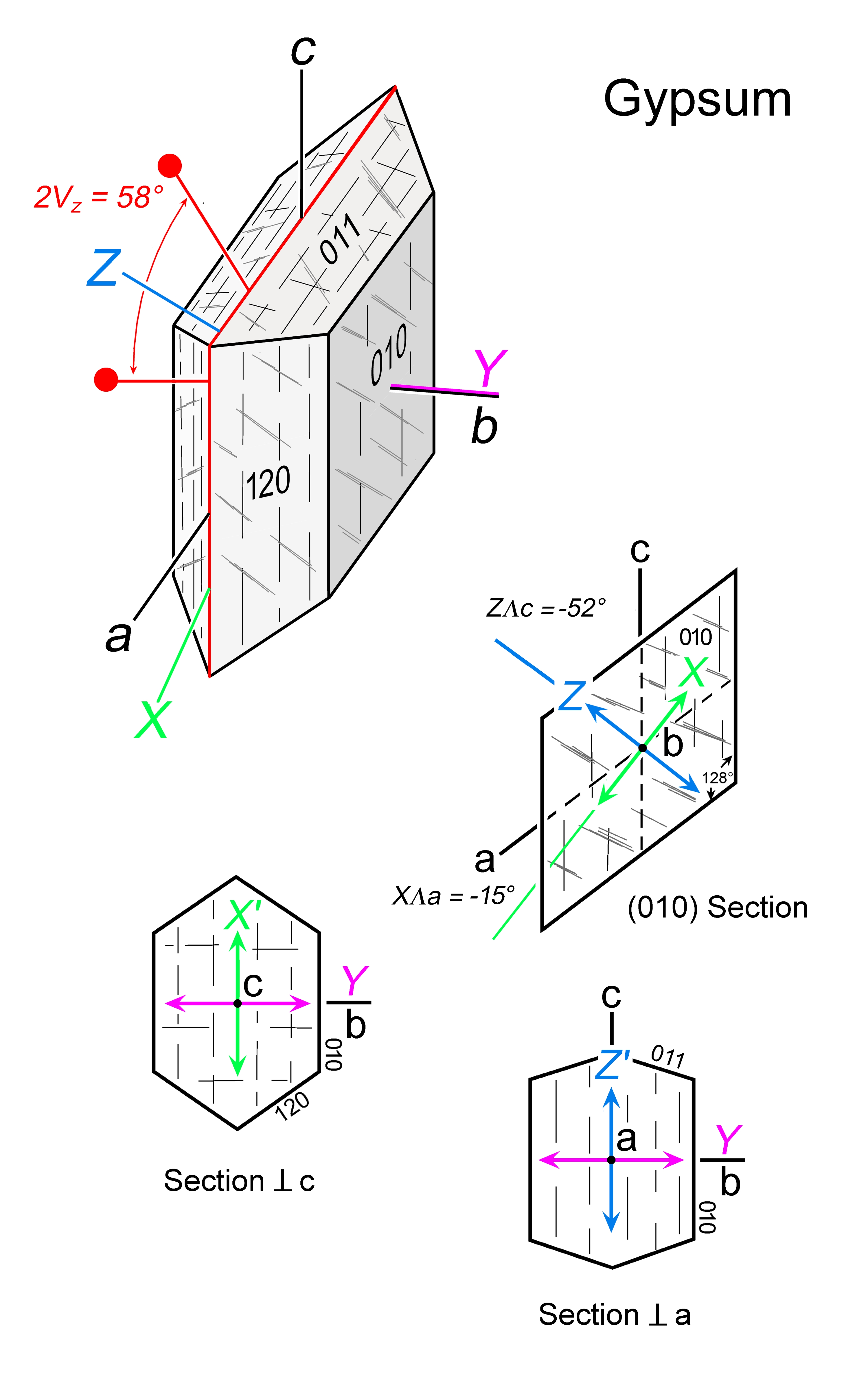

 Images
Images 
