|
| Formula | Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | X near c, Y ~ a, Z = b |
| | Optical plane | Orthogonal to (010), close to (100) |
| | Relief | Low-positive |
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.538 -1.550
|
|
ny = 1.575 -1.594
|
|
nz = 1.575 -1.600
|
|
| n increases with Fe content |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.04 - 0.05 |
| | | |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 0 - 30° |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+) |
| | Interference figure | Acute bisectrix figures with multiple isochromes in sections ⊥ c |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Platy, flaky, randomly oriented grains in aggregates |
| | | Surface | Subhedral to anhedral |
| | Cleavage | {001} perfect |
| | Twinning | Not observed |
| | Extinction | Essentially straight; “bird’s-eye-maple” structure |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Stable under surface conditions |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | Talc schists, talc-kyanite “whiteschists”, metamorphosed siliceous dolomites |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | Hydrothermally altered ultramafic rocks |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Habit, single perfect cleavage, high Δn and lack of colour, occurrence; “bird’s-eye-maple” structure (a property shared with other sheet silicates).
Pyrophyllite, muscovite and pure phlogopite may be hard to distinguish optically from talc. The very soft talc surface is easily scratched during thin section preparation. |
| | Additional comments | |
|
|

 Images
Images 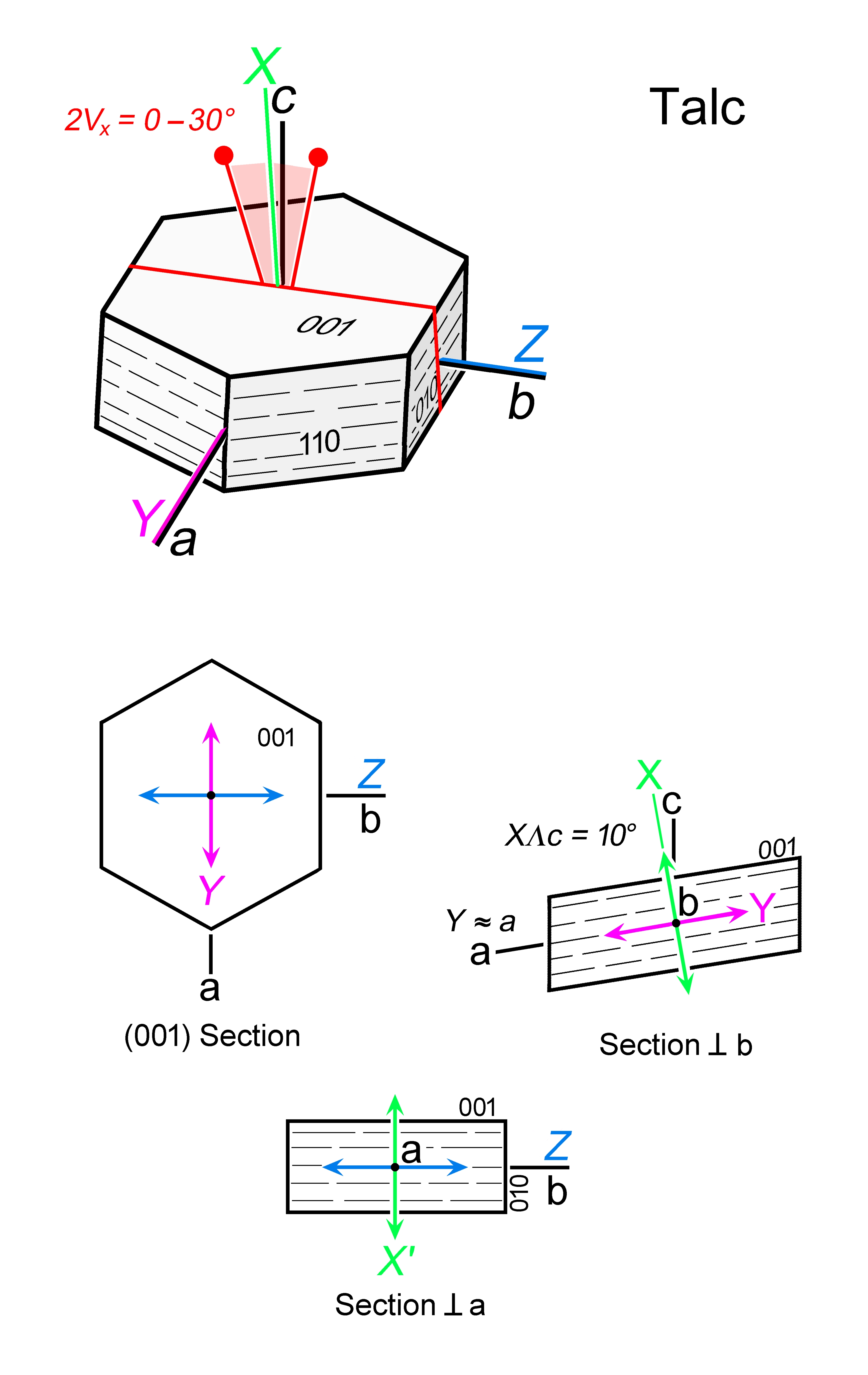


 Images
Images 
