|
| Formula | Ca2(Al,Fe3+,Mn3+)3O(Si2O7)(SiO4)OH |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive or negative |
| | Optical orientation | X Λ c and Z Λ a vary, Y = b |
| | Optical plane | (010) |
| | Relief | High |
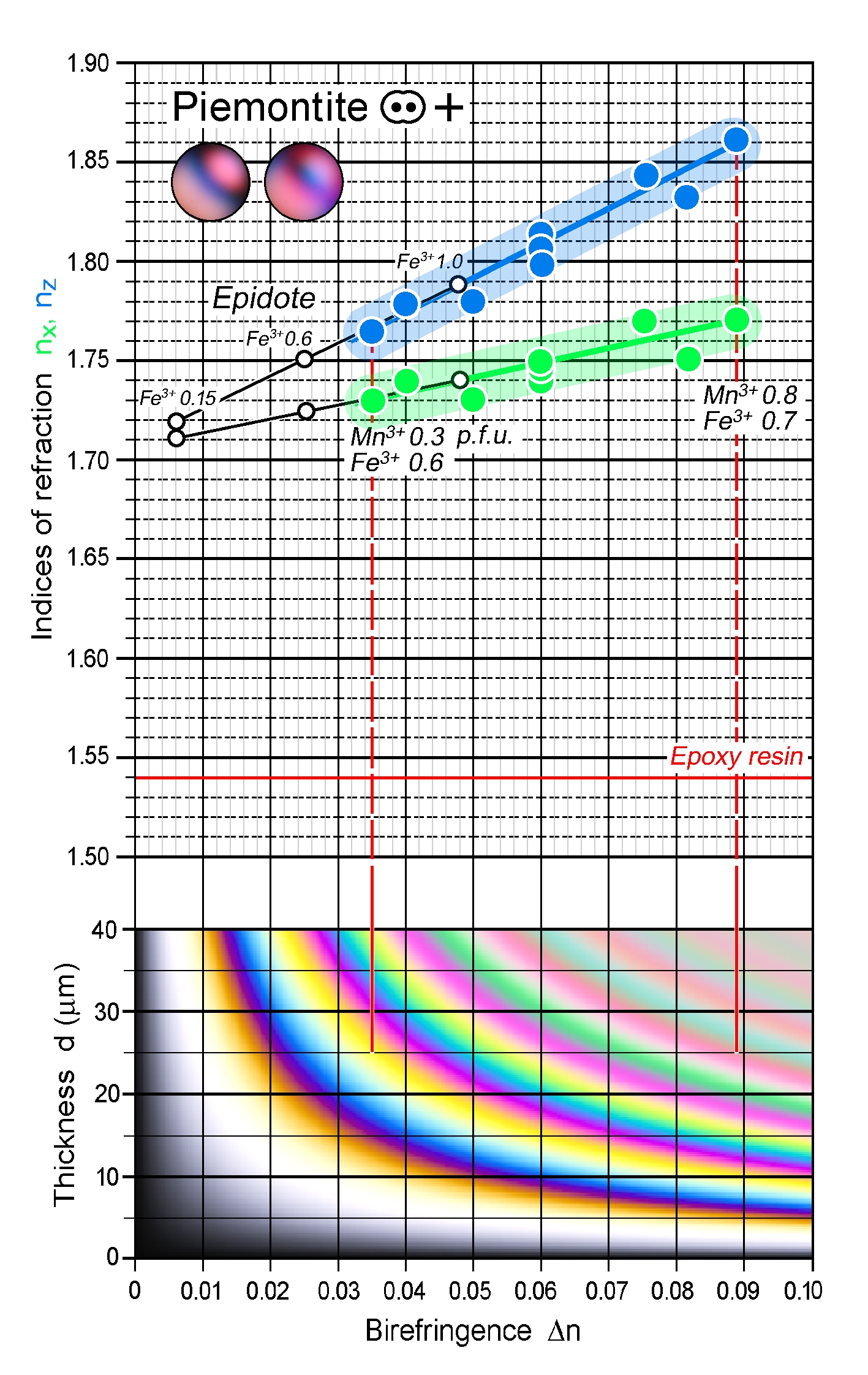
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.725 -1.794
|
|
ny = 1.730 -1.807
|
|
nz = 1.750 -1.832
|
|
| n increases with increasing Fe3+ and Mn3+ substitution for Al |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.025 - 0.082 |
| | | Δn increases with increasing Fe3+ and Mn3+ substitution for Al |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 70 - 90° |
| | 2Vz
= 90 - 64° |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+) and length-fast, l (-) for crystals elongate in b (= Y) |
| | Interference figure | Isogyres distinct to diffuse, depending on Δn. Optic axis dispersion commonly strong. Masking of interference colours by strong mineral colour. |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Distinctly to strongly coloured and pleochroic. X: pale yellow to orange, Y, Z: red, purple, Colour zoning may occur. |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Granular, columnar, bladed, acicular. Crystals are elongate parallel to b. |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral |
| | Cleavage | {001} perfect |
| | Twinning | Lamellar twins on {100} rare |
| | Extinction | Straight to (h0k) faces and to {001} cleavage traces in elongate sections (long axis = b). X-Z sections of max Δn show inclined extinction to all morphological elements. |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Relatively stable |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | Mn-rich phyllites, schists, blueschists |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | Spherulites in felsic to intermediate volcanic rocks; hydrothermal Mn deposits |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Colour, high n, high Δn, association with other Mn minerals |
| | Additional comments | |
|
|

 Images
Images 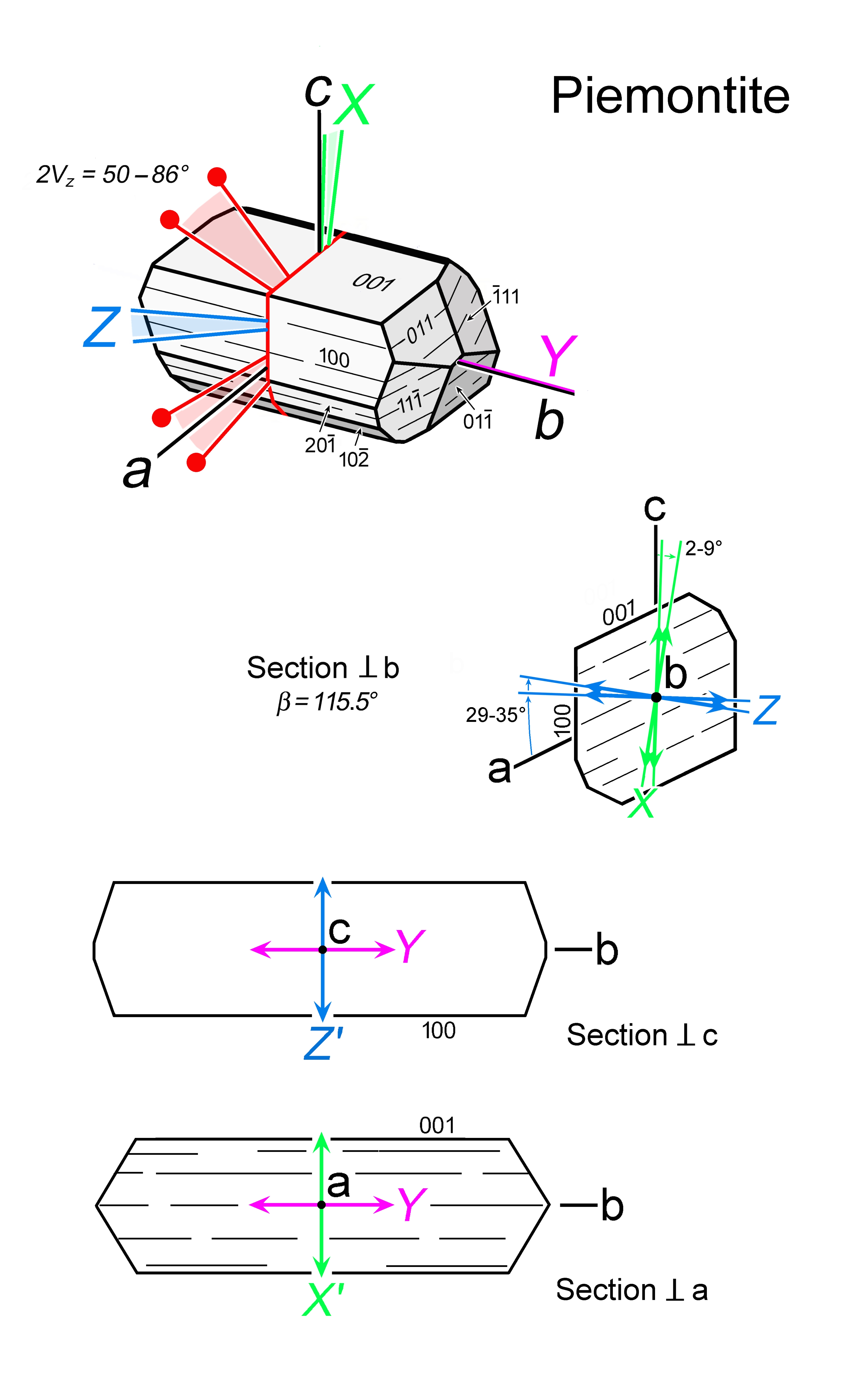

 Images
Images 
