|
| Formula | NaAl2(AlSi3O10(OH)2 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | X near c, Y ~ a, Z = b |
| | Optical plane | Approx. (100) |
| | Relief | Low- to moderate-positive |
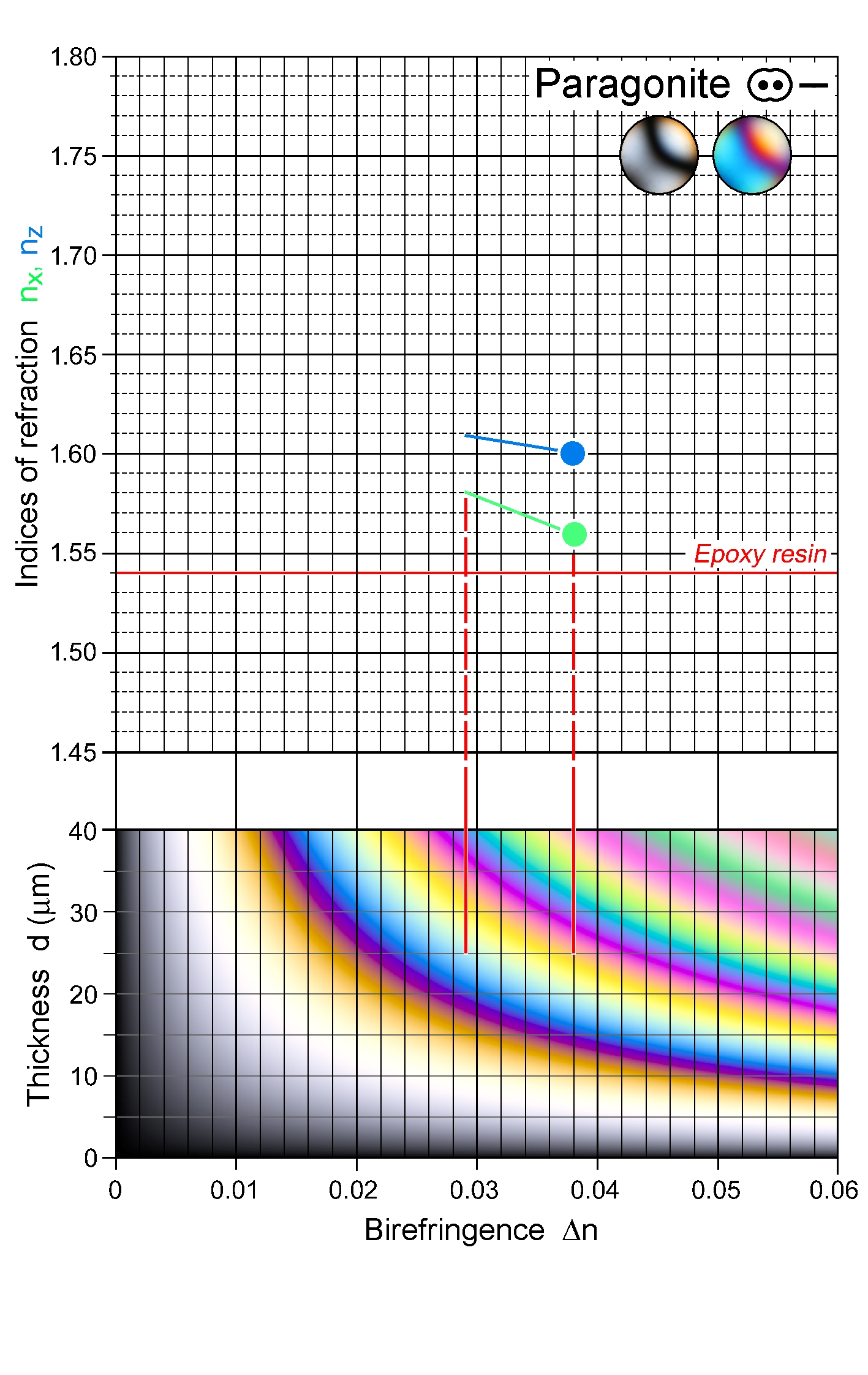
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.564 -1.580
|
|
ny = 1.594 -1.609
|
|
nz = 1.600 -1.609
|
|
| |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.028 - 0.038 |
| | | |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 0 - 45°, 3T variety 0° |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+) |
| | Interference figure | Acute bisectrix figures with multiple isochromes in sections orthogonal to c |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Flaky to platy |
| | | Surface | Typically subhedral with well-developed (001) crystal faces |
| | Cleavage | {001} perfect |
| | Twinning | |
| | Extinction | Straight or nearly straight to {001} traces; max angle ca. 3°
Characteristic “bird’s-eye-maple” structure |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Highly weathering-resistant; sericite (Na- or K-) is itself a common alteration product |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | Phyllites and schists; blueschist-facies rocks |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Habit, single perfect cleavage, high Δn and lack of colour; “bird’s-eye-maple” structure (a property shared with other sheet silicates).
Talc, pyrophyllite and pure phlogopite may be hard to distinguish optically from paragonite. Occurrence may give clues. Paragonite and muscovite/phengite cannot be distinguished optically, but are easily distinguishable by XRD. |
| | Additional comments | |
|
|

 Images
Images 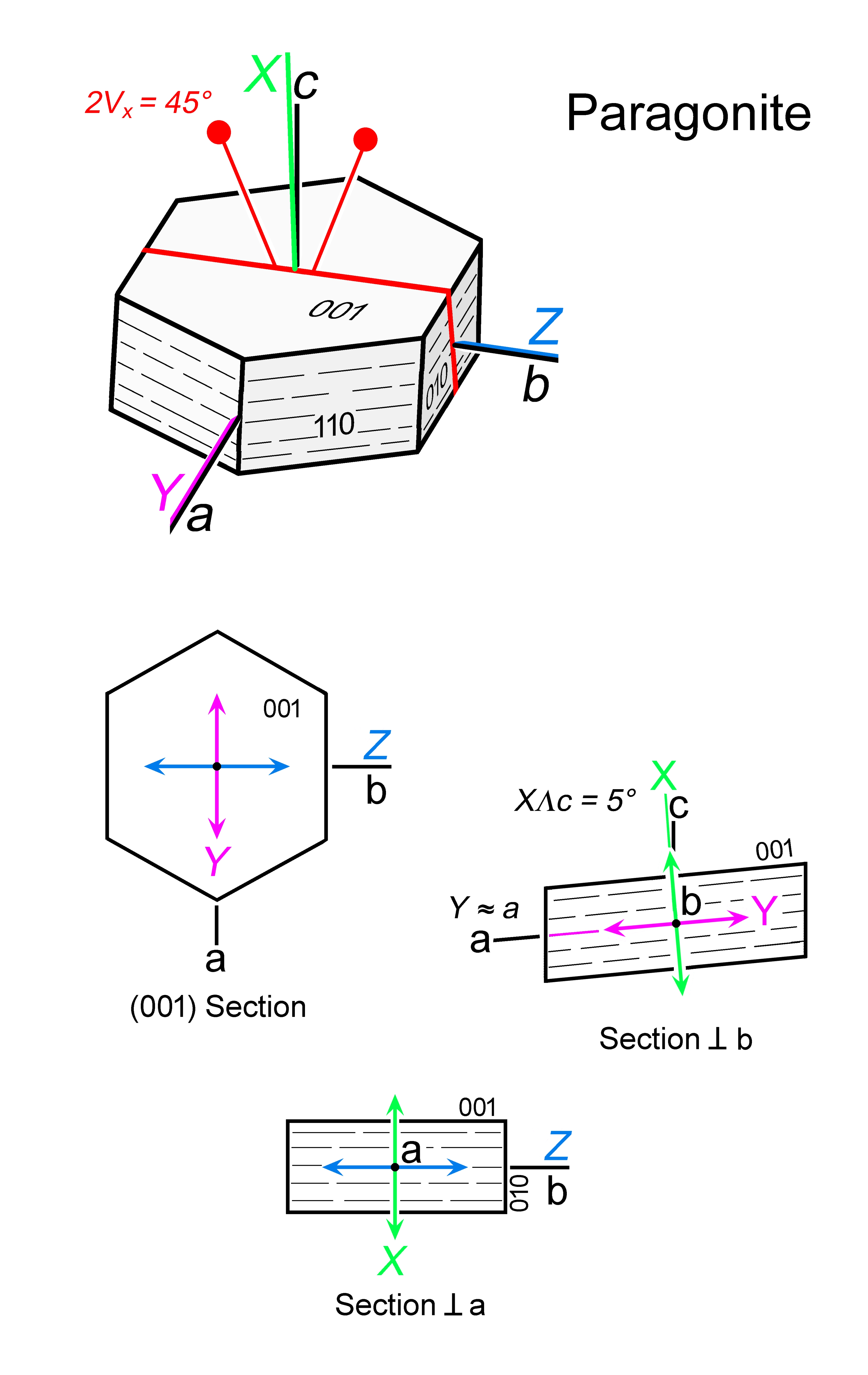

 Images
Images 
