|
| Formula | (K,Na)AlSi3O8 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | a near X, b = Z, c near Z |
| | Optical plane | Approx. parallel to (001) |
| | Relief | Low negative |
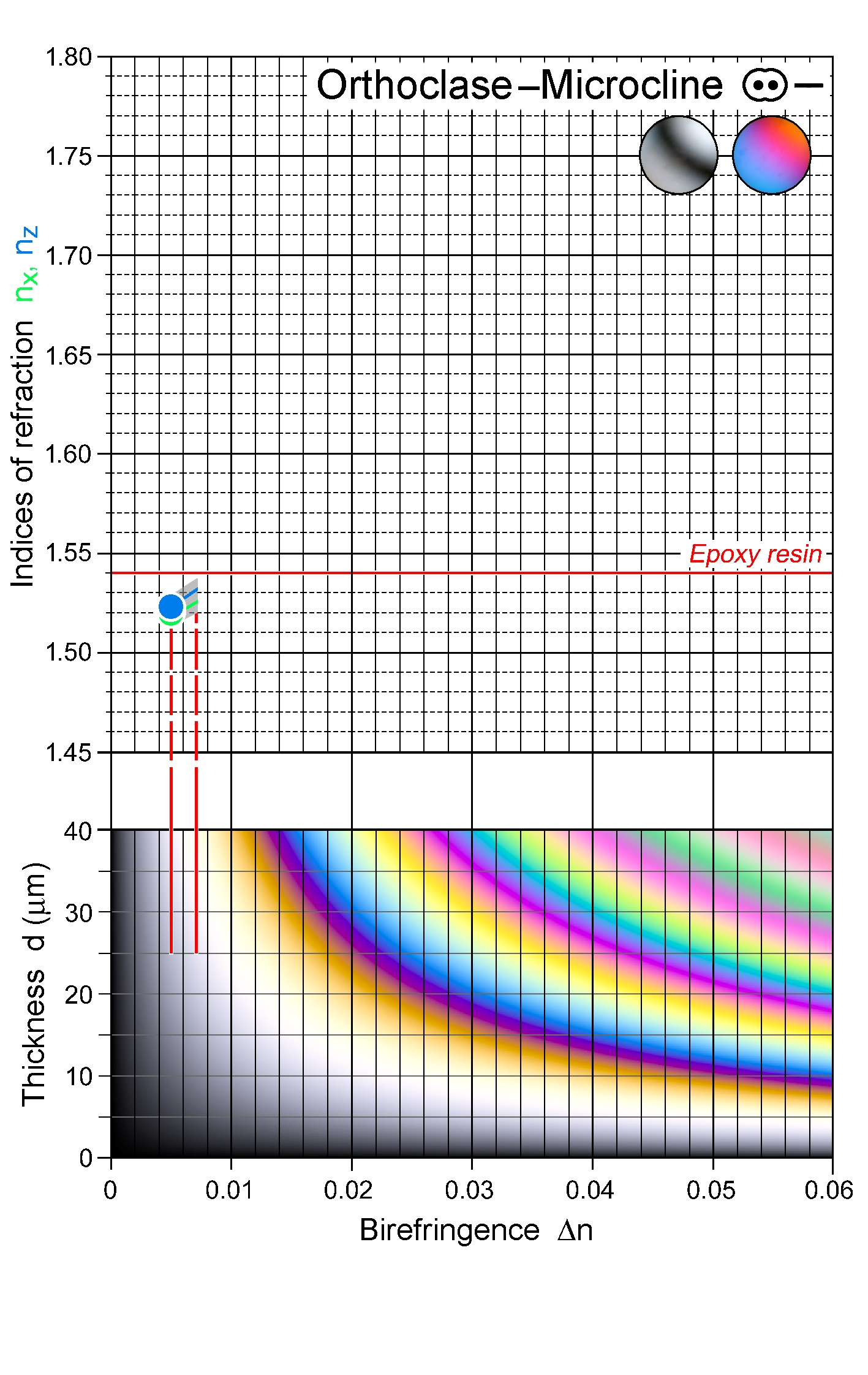
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.514 -1.526
|
|
ny = 1.518 -1.530
|
|
nz = 1.521 -1.533
|
|
| - |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.005 - 0.008 |
| | | - |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 65 - 86° |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | Length-fast, l (-) |
| | Interference figure | Optic axis figures are commonly impractical due to intense twinning. Highly variable 2V, broad isogyres on low-Δn grey background. |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless. May be clouded by alteration minerals. |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Granular, tabular, elongate ∥ c or a. As blebs of unmixed Kfs in anti-perthite. |
| | | Surface | Commonly anhedral |
| | Cleavage | {001} perfect, {010} distinct, intersecting at about 90° |
| | Twinning | Typically 2 sets of diffuse lamellar twins orthogonal to each other (“cross-hatched twinning”, “tartan twinning”), one set which are {010} albite twins, the other pericline twins with a twin plane at 35° to {001}.
Simple {010} Carlsbad twins (twin axis [001]
Simple Baveno or Manebach twins are less common.
|
| | Extinction | Cannot be verified sensibly in twinned crystals |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Product of phase transition orthoclase to microcline. Product of unmixing in anti-perthite. |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Kaolinite, illite, sericite |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Felsic plutonic rocks incl. pegmatites |
| | | Met | Low-grade to high-grade rocks; greenschists, amphibolites, abundant in felsic gneisses and high-grade metapelitic gneisses |
| | | Sed | Detrital in sediments and sedimentary rocks, particularly in immature clastic deposits; authigenic in diagenetic environments |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Low negative n, low Δn, cross-hatched twinning |
| | Additional comments | Unmixing of potassic alkalifeldspar is common. Albitic Plg may form stringers or blebs inside the host crystal (‘perthite’). Most microcline in igneous rocks is perthitic, even if only sub-microscopically.
Cross-hatched twinning is thought to result from lattice strain caused by the transition from monoclinic orthoclase to triclinic microcline during cooling. All microcline from igneous rocks is secondary, inverted from orthoclase, as microcline is not a stable phase at super-solidus temperatures.
The diagram below shows the relationship between 2VX, composition and Al-Si order/disorder for alkalifeldspars.
|
|
|

 Images
Images 


 Images
Images 

