|
| Formula | LiAlSi2O6 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive |
| | Optical orientation | a near X, b = Y, c near Z |
| | Optical plane | (010) |
| | Relief | Moderate to high |
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.648 -1.668
|
|
ny = 1.655 -1.671
|
|
nz = 1.662 -1.682
|
|
| n decreases with increasing Na; increases with increasing Fe3+ replacing Al |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.014 - 0.027 |
| | | Δn increases with increasing Na; increases with increasing Fe3+ replacing Al |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
|
| | 2Vz
= 54 - 68° |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+) |
| | Interference figure | Acute bisectrix figures in {100} sections, with few isochromes |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless; Mn-bearing variety kunzite is colourless to purple pleochroic |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Long-prismatic to elongate-tabular, also acicular; eight-sided sections ⊥ c |
| | | Surface | Anhedral to euhedral |
| | Cleavage | 2 sets {110} distinct, at 93 and 87° (seen in sections ⊥ c); parting on {010}. In prismatic sections, the traces of the two principal cleavage sets are parallel. |
| | Twinning | Twins on {100} may occur |
| | Extinction | Inclined, cɅZ = 20 - 27°; c ∥ cleavage traces and prism faces. Symmetrical extinction to {110} cleavage and {110} faces in {001} sections. |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Lepidolite, albite, eucryptite |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Granite pegmatites, aplites |
| | | Met | Rarely in high-grade gneisses |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Low to moderate Δn, small extinction angles in maximum birefringence sections, characteristic pyroxene cleavage observed in sections ⊥ c. |
| | Additional comments | Spodumene occurs most commonly in pegmatites where crystals can be very large |
|
|

 Images
Images 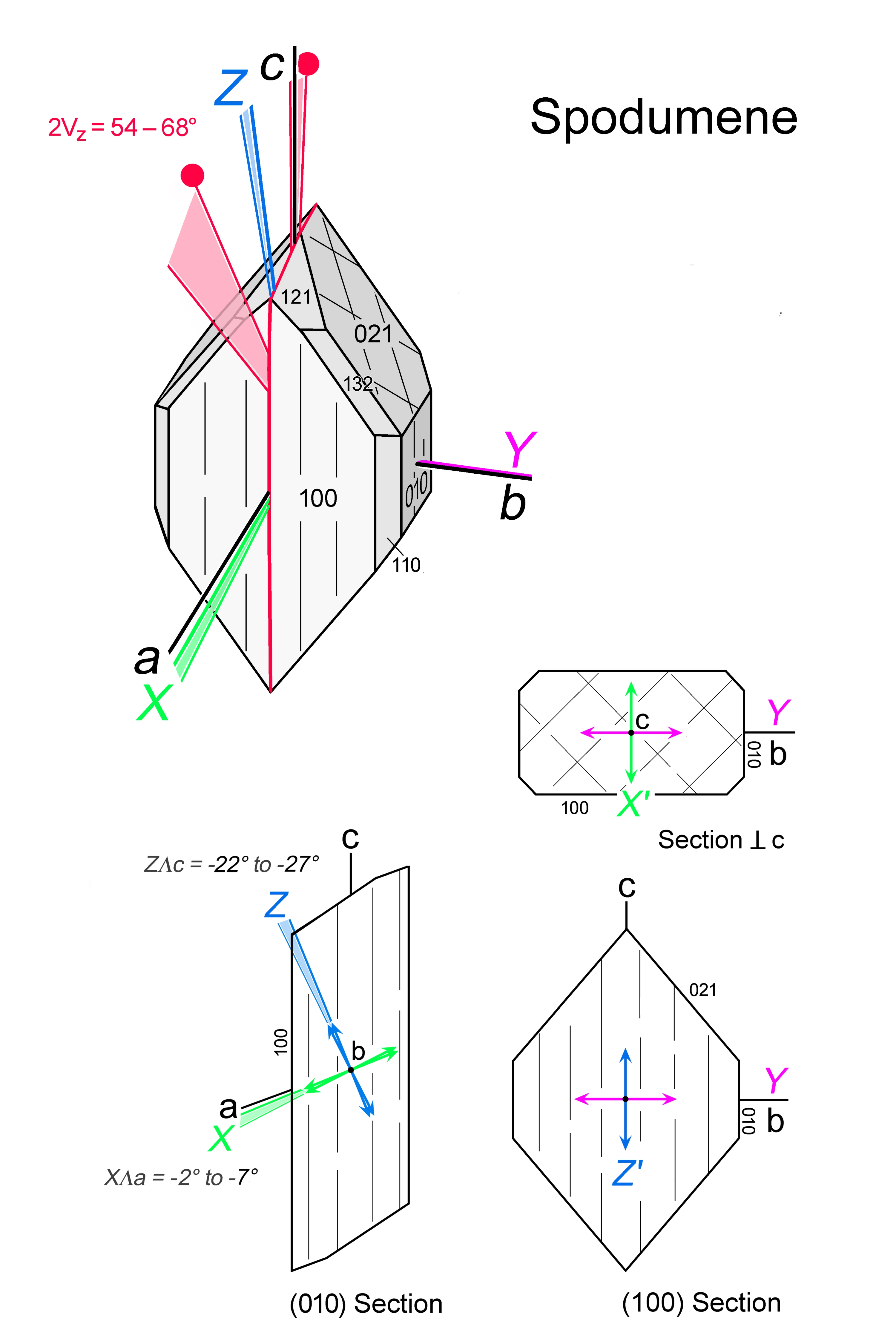


 Images
Images 
