|
| Formula | C |
| | Optic class & sign | Isotropic |
| | Relief | Extreme |
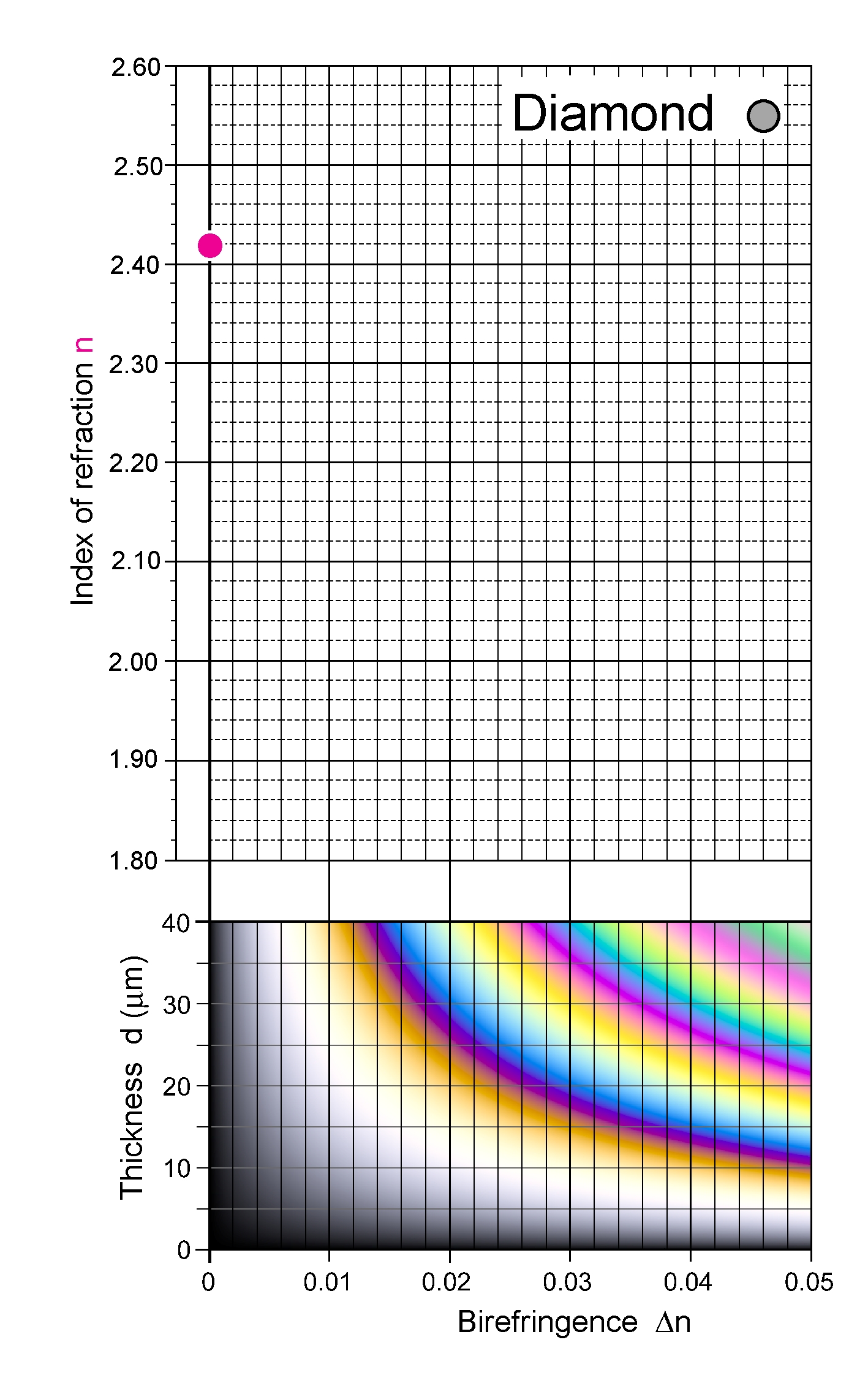
| | Refractive Index | 2.419
|
|
| - |
| | Birefringence | May show weak birefringence if strained
|
| | Colour | Colourless, pale yellow, brown, or green |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Octahedral, dodecahedral, cubic, tetrahedral |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral |
| | Cleavage | {111} perfect |
| | Twinning | Contact twins on {111} and penetration twins; also lamellar or cyclic twins |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Partial or complete replacement by graphite |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Stable under surface conditions |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | Kimberlites, lamproites (pipes and dikes) |
| | | Met | Ultra-high pressure rocks (metapelites, calcsilicate rocks, eclogites); shock-metamorphic transformation of carbonaceous matter at meteorite impact sites |
| | | Sed | In heavy mineral fraction of gravels and sands where diamondiferous rocks occur in the catchment area |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | Carbonaceous achondrite, iron meteorites |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Restricted occurrence, crystal form, extreme relief, extreme hardness. In thin sections, minute fragments can leave radial scratch marks emanating from a diamond grain, as a result of surface polishing |
| | Additional comments | Thin section preparation difficult due to diamond’s extreme hardness |
|
|

 Images
Images 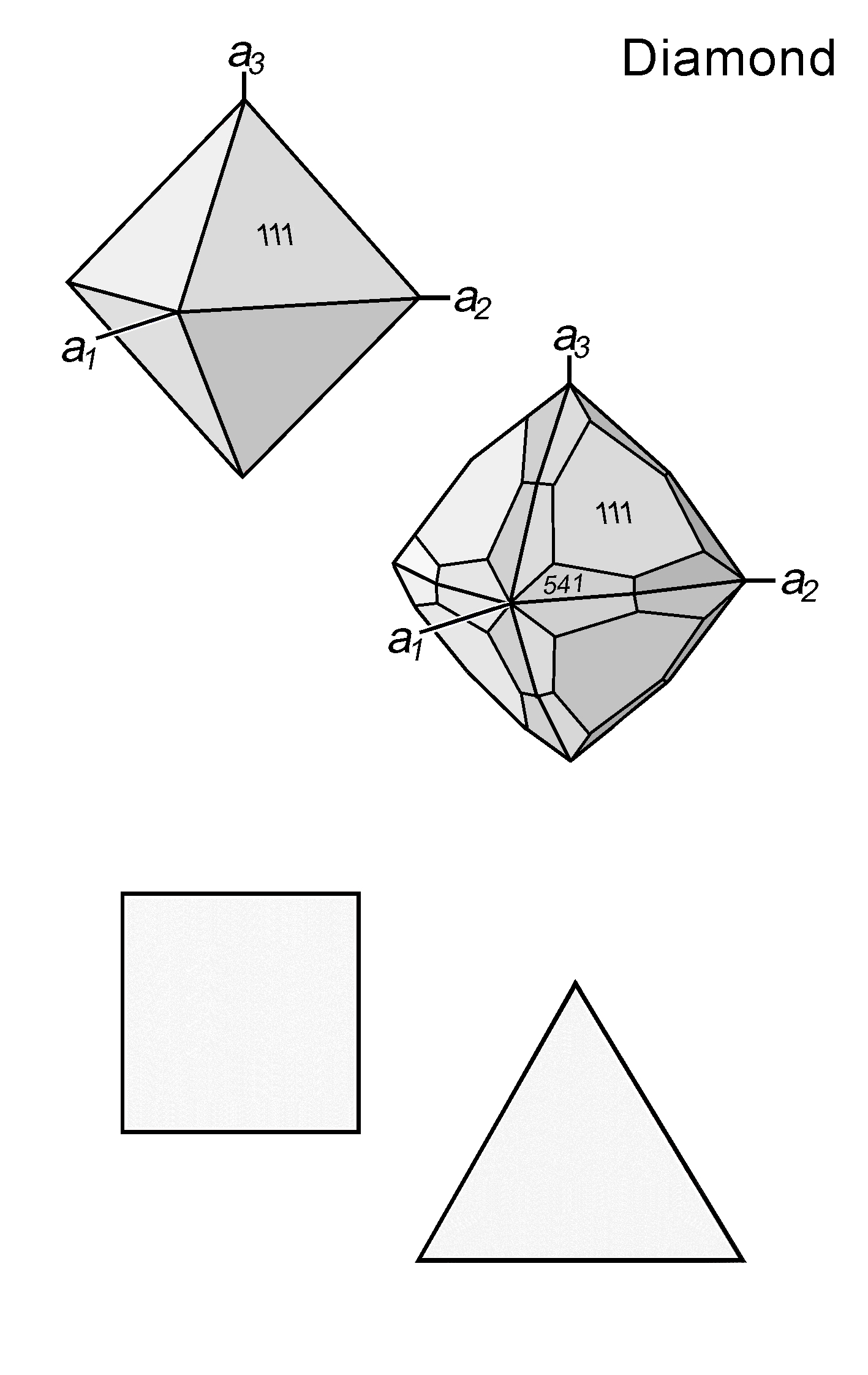

 Images
Images 
