|
| Formula | SiO2 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive |
| | Optical orientation | X = b, Y near a, Z near c |
| | Optical plane | Orthogonal to (010) |
| | Relief | Moderate-positive |
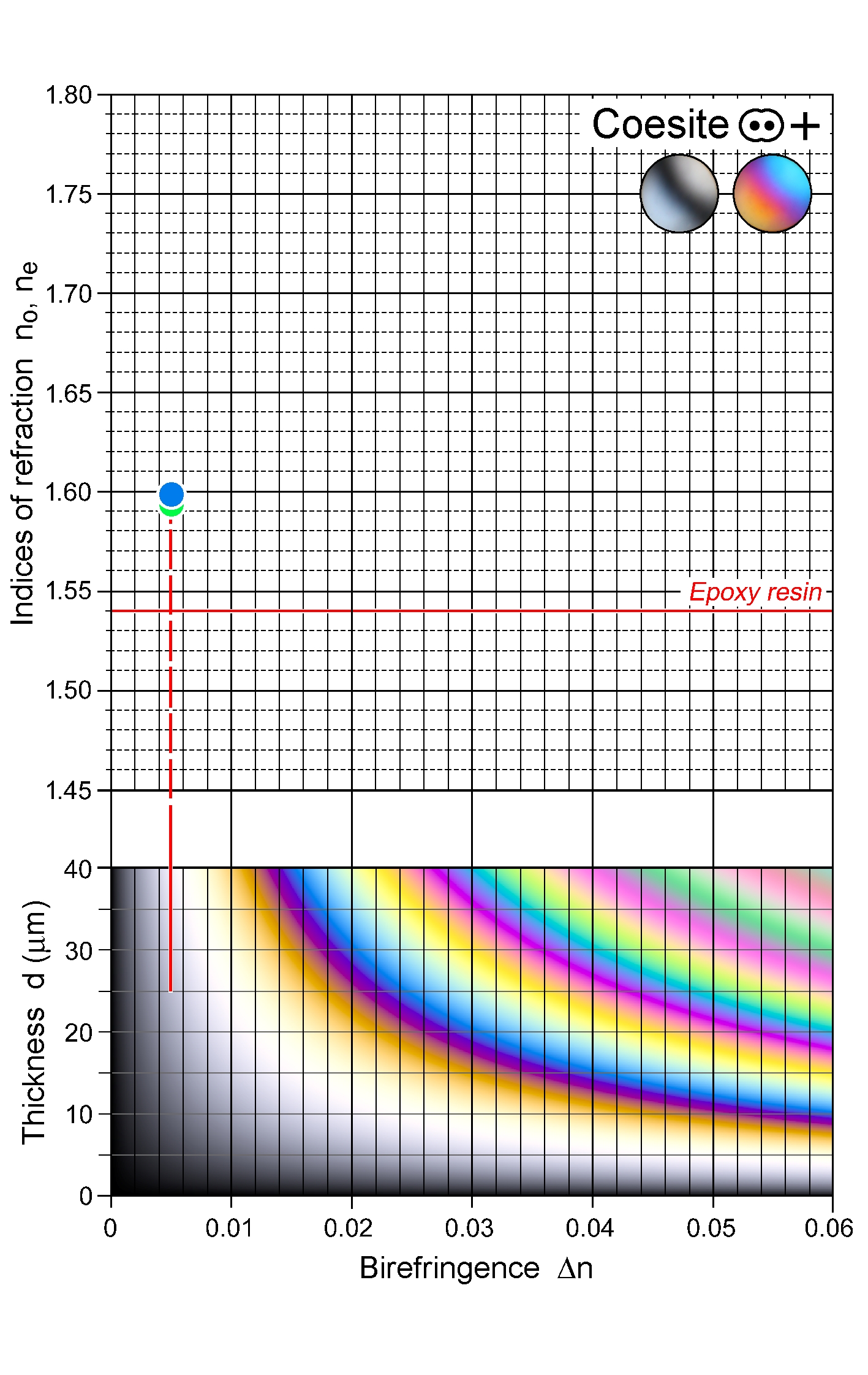
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.594
|
|
ny = 1.596
|
|
nz = 1.599
|
|
| - |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.005 |
| | | - |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
|
| | 2Vz
= 64° - |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+) |
| | Interference figure | |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | |
|
|
| Form | Habit | |
| | | Surface | |
| | Cleavage | {010} |
| | Twinning | |
| | Extinction | |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Retrograde paramorphic transformation to quartz is common, with characteristic palisade structure. Complete replacement may show a core domain of mosaic quartz. Breakdown to quartz typically results in radial expansion cracks in the host mineral around coesite inclusions. |
| | Alteration / decomposition | |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | Shock-metamorphosed rocks related to meteorite impacts; ultrahigh-pressure rocks containing free silica |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Partial transformation to quartz; n, very low Δn |
| | Additional comments | Ultrahigh-pressure indicator mineral; commonly only preserved as inclusions in other UHP-formed minerals (e.g., garnet, pyroxene, diamond) |
|
|

 Images
Images 

 Images
Images 
