|
| Formula | (Na,K,Ca0.5,Sr0.5,Ba0.5,Mg0.5)6Al6Si30O72 ∙ 20H2O |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive or negative |
| | Optical orientation | X = b, Y near a, Z near c |
| | Optical plane | Optic plane ⊥ (010l) |
| | Relief | Moderate-negative |
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.473 -1.491
|
|
ny = 1.475 -1.493
|
|
nz = 1.478 -1.497
|
|
| n increases with CaAl substituting for NaSi |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.003 - 0.006 |
| | | |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 85 - 90° |
| | 2Vz
= 90 - 32° |
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+), for elongate cross-sections ⊥ (010), for the optical orientation shown; other indicatrix orientations show length-fast, I (-) |
| | Interference figure | |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | - |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Platy |
| | | Surface | |
| | Cleavage | {010} |
| | Twinning | Commonly not twinned |
| | Extinction | Z∧c or trace of {100} = 18 – 23°; higher for K-Cpt |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | Sediments incl pyroclastics at lowest-grade burial metamorphism, also from devitrification |
| | | Sed | Diagenetic in submarine sediments, lake deposits |
| | | Hyd | Cavities and veins in basalt, andesite and rhyolite |
| | | Other | |
|
|
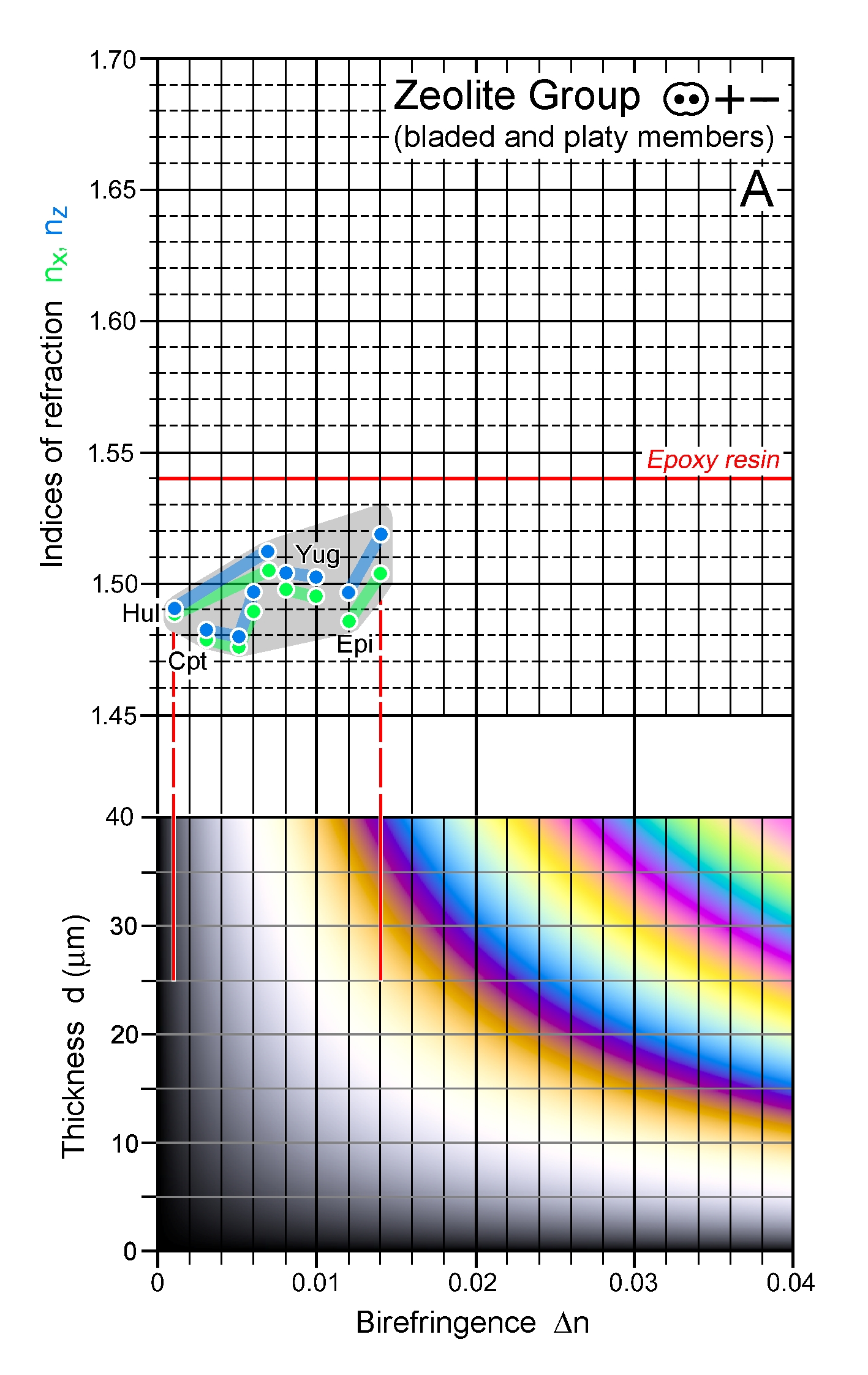
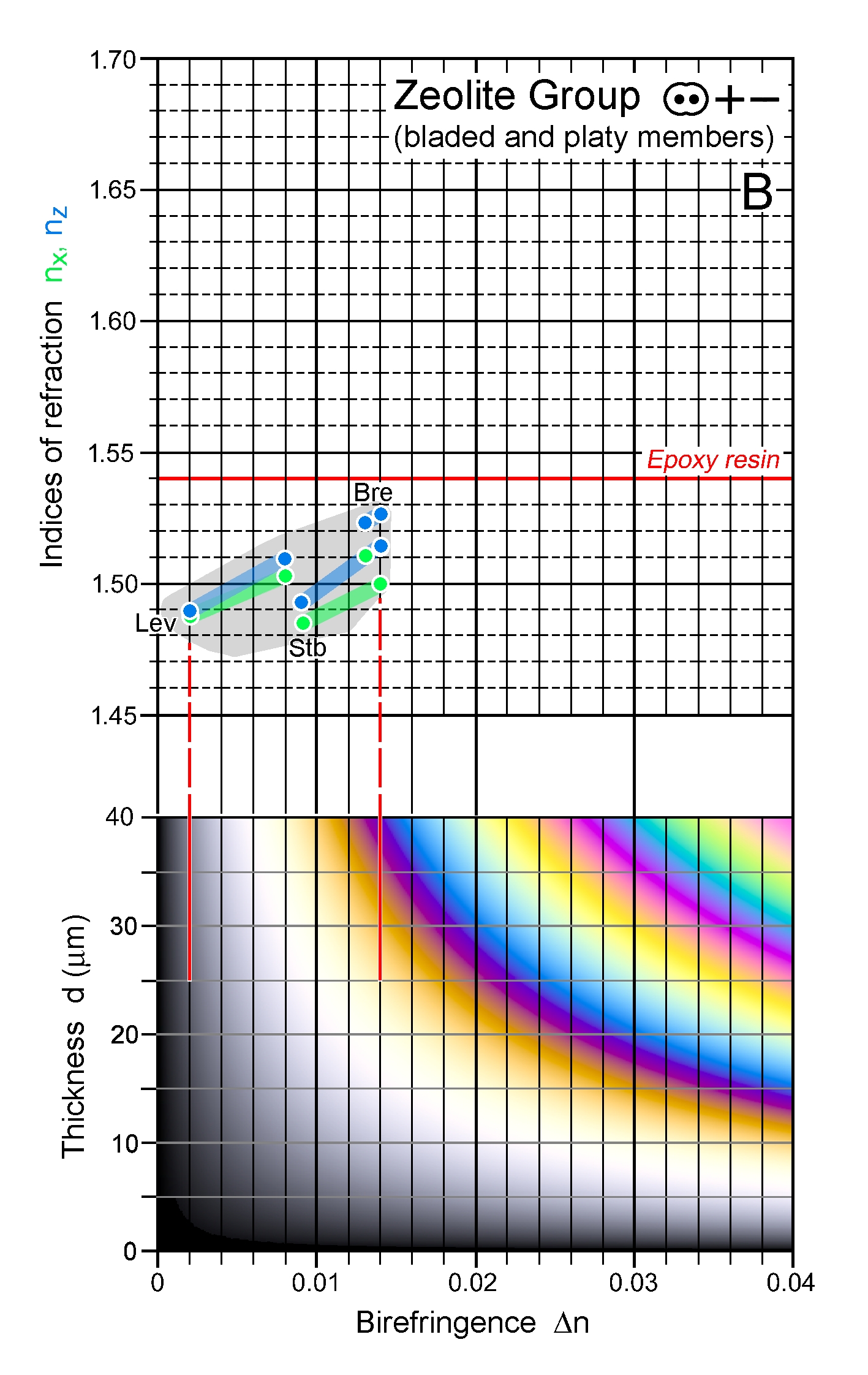
| Distinctive properties | Common zeolite. Very low n, very low to low Δn. Heulandite and clinoptilolite are difficult to distinguish from each other, but heulandite has commonly higher refractive indices. |
| | Additional comments | n-Δn charts A, B: Bre - brewsterite, Cpt - clinoptilolite, Epi - epistilbite, Hul - heulandite,
Lev - levyne, Stb - stilbite, Yug - yugawaralite |
|
|

 Images
Images 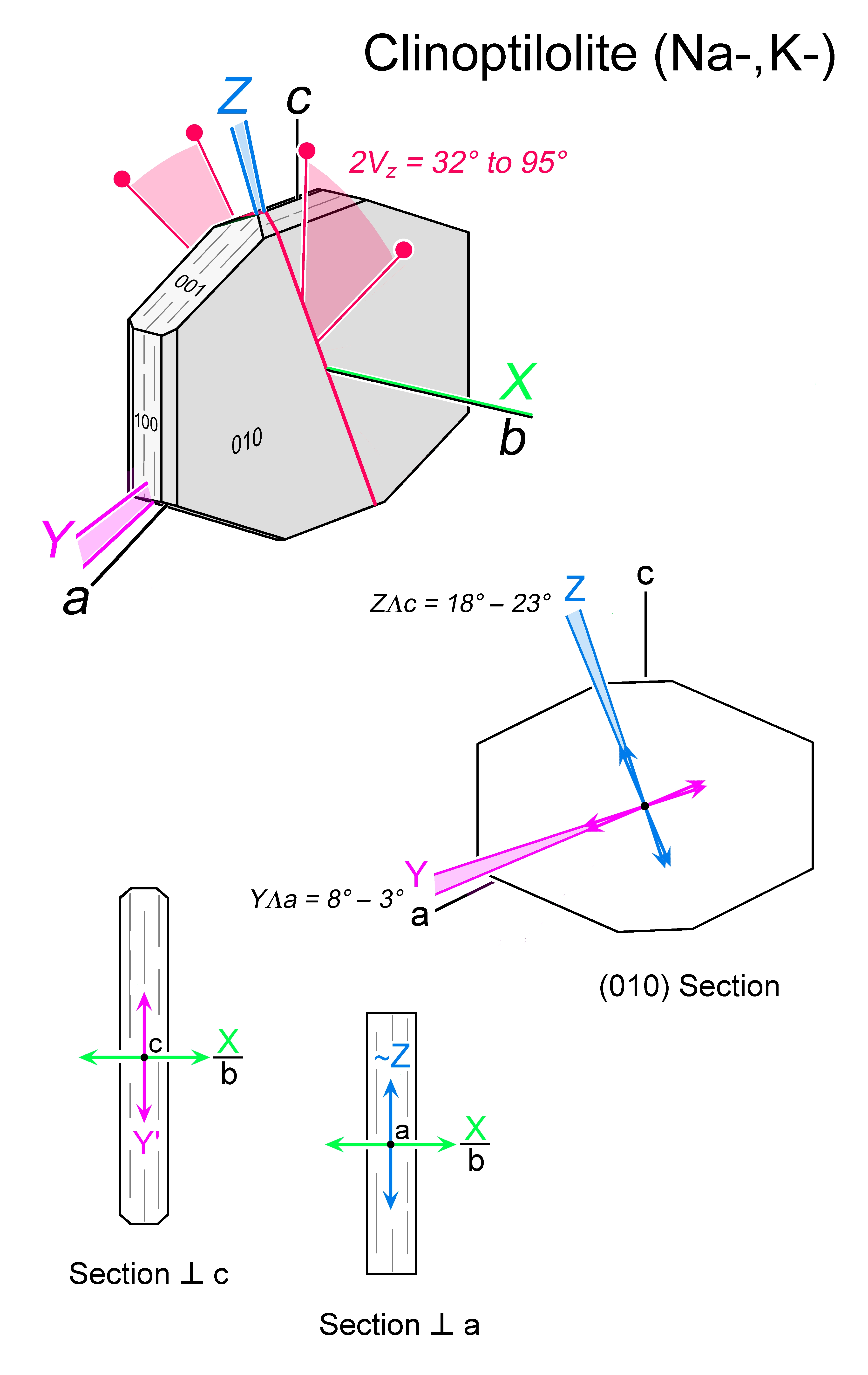

 Images
Images 

