|
| Formula | Ca2Al4Si4O16 • 9H2O |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | X at a high angle to a, Y = b, Z at a high angle to c |
| | Optical plane | (010) |
| | Relief | Low-negative to low-positive |
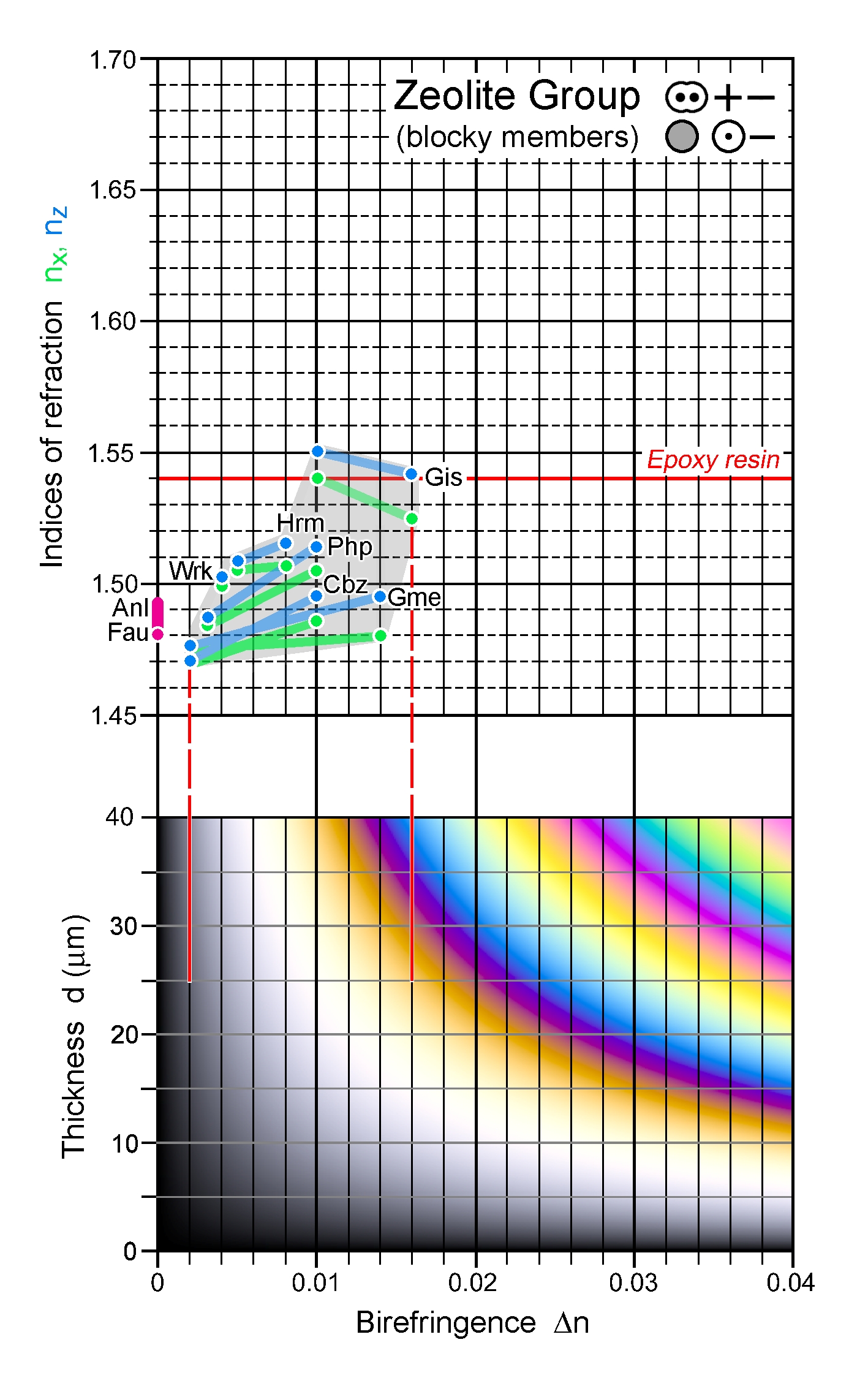
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.525 -1.540
|
|
ny = 1.531 -1.544
|
|
nz = 1.541 -1.550
|
|
| n decreases with substitution of Ca by Na and K |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.010 - 0.016 |
| | | Δn decreases with substitution of Ca by Na and K |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 82 - 86° |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | |
| | Interference figure | |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | - |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Dipyramidal crystals, radiating aggregates; twinning results in octahedra-like pseudo-tetragonal or pseudo-orthorhombic forms; cross-sections showing two pairs of sectors with different optical-orientations |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to subhedral |
| | Cleavage | {232} |
| | Twinning | Penetration twins; “fourlings” with twin planes approximately {100} and {001} |
| | Extinction | In principle, symmetrical to crystal faces in sections orthogonal to c or a. Not readily evaluated due to complex twinning and patchy extinction. |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | |
| | | Sed | Vesicle fillings in silica-undersaturated volcanics, such as nepheline basalt, leucitic basalt, olivine basalt and leucite tephrite; miarolitic and other cavities in altered granite and nepheline syentite; hydrothermal veins |
| | | Hyd | |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Habit, comparatively high n and Δn in relation to other blocky zeolites; uncommon zeolite
Note: Reliable identification of zeolite species may require chemical analysis, X-ray diffraction, and/or DTA
|
| | Additional comments | Crystal-optical relationships shown here are based on Nawaz (1980), Min. Mag. 43, 841-844.
n-Δn chart: Anl – analcime, Cbz – chabazite, Fau – faujasite, Gis - gismondine,
Gme – gmelinite, Hrm – harmotome, Php – phillipsite, Wrk - wairakite |
|
|

 Images
Images 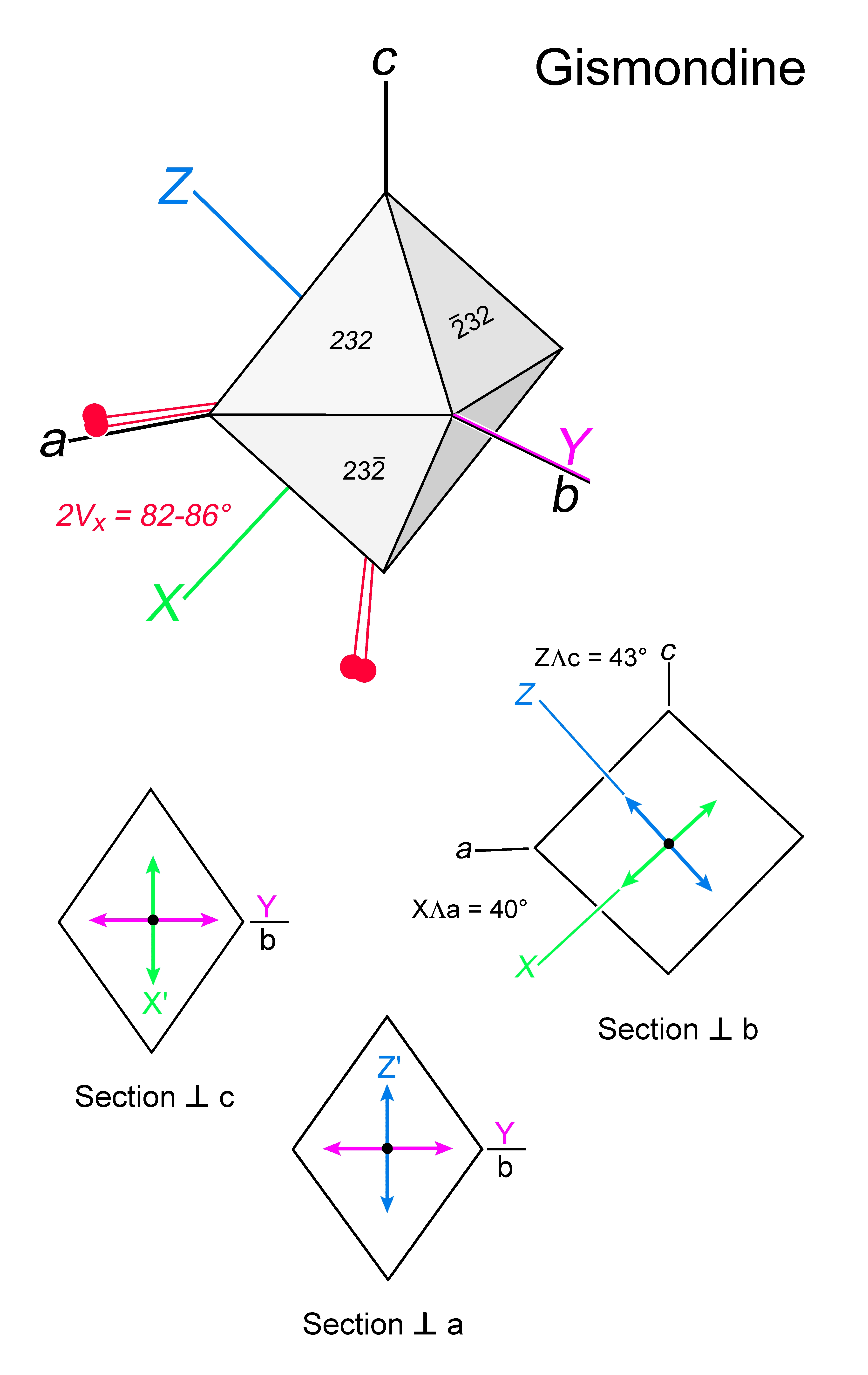

 Images
Images 
