|
| Formula | (K,Na,Ca)2(Si,Al)8O16 • 6H2O |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive |
| | Optical orientation | X = b, Y at a high angle to a, Z near c |
| | Optical plane | Orthogonal to (010) |
| | Relief | Moderate- to low-negative |
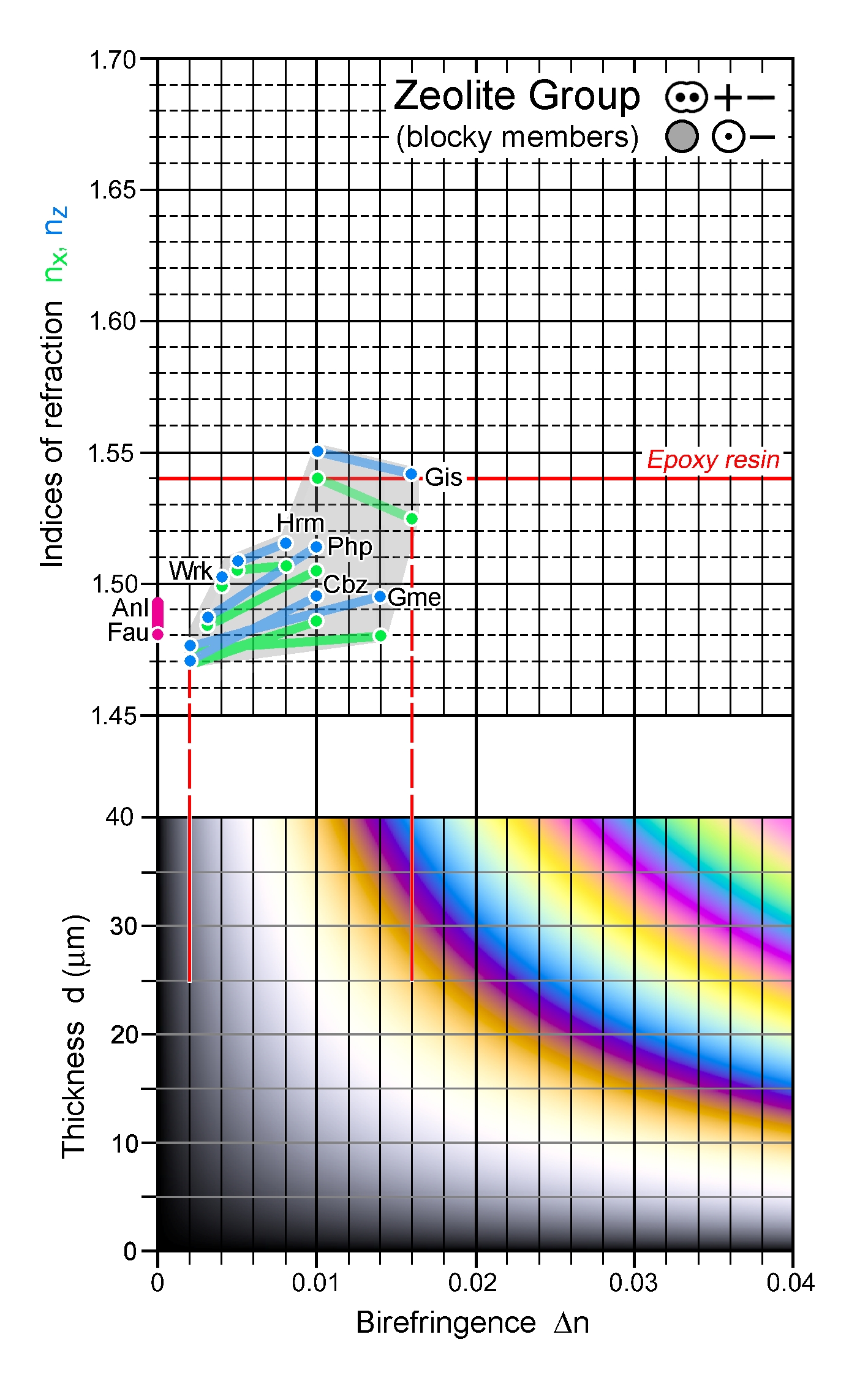
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.483 -1.504
|
|
ny = 1.484 -1.509
|
|
nz = 1.486 -1.514
|
|
| n decreases with increasing Si content |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.003 - 0.010 |
| | | |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
|
| | 2Vz
= 60 - 80° |
| | Sign of elongation | |
| | Interference figure | Broad, diffuse isogyres; relatively high 2V |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | - |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Granular, columnar-prismatic, radiating aggregates; twinning results in pseudo-orthorhombic, pseudo-tetragonal and pseudo-cubic forms |
| | | Surface | Commonly euhedral to subhedral |
| | Cleavage | {010}, {100} |
| | Twinning | Generally twinned; single and double penetration twins on {001}, {201} and {011} |
| | Extinction | Inclined to crystal faces and twin planes in random sections |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | |
| | | Sed | Saline lake deposits, hot-spring deposits; authigenic in deep-sea sediments, altered tuffs |
| | | Hyd | Vesicle and fracture fillings in silica-deficient volcanic rocks (including basalts, phonolites, trachytes) |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Habit and twinning
Note: Reliable identification of zeolite species may require chemical analysis, X-ray diffraction, and/or DTA |
| | Additional comments | n-Δn chart: Anl – analcime, Cbz – chabazite, Fau – faujasite, Gis - gismondine,
Gme – gmelinite, Hrm – harmotome, Php – phillipsite, Wrk - wairakite |
|
|

 Images
Images 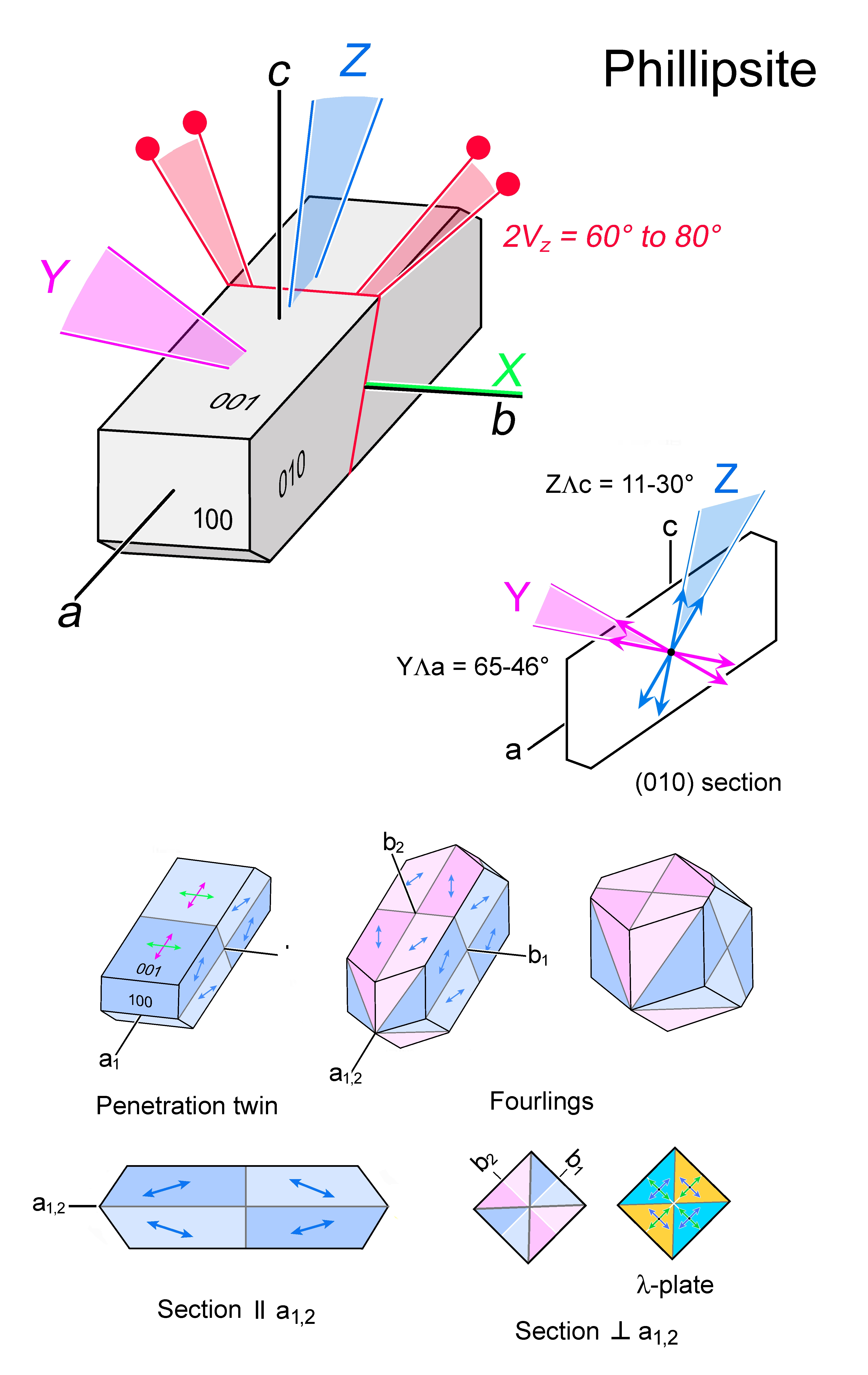

 Images
Images 
