|
| Formula | CaAl2Si4O12 ∙ 2H2O |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial positive or negative |
| | Optical orientation | X = b, Y ≈ a, Z ≈ c |
| | Optical plane | (100) |
| | Relief | Low-negative |
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.498
|
|
ny = 1.500
|
|
nz = 1.502
|
|
| |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.004 |
| | | |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 75 - 90° |
| | 2Vz
= 90 - 70° |
| | Sign of elongation | Not applicable |
| | Interference figure | Impractical due to very low Δn and twinning |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | - |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Trapezohedral. The crystal shape of monoclinic wairakite is very close to a cubic symmetry as in analcime. For simplicity, a cubic shape and corresponding crystallographic orientation are shown in the graphic presentation. |
| | | Surface | Commonly subhedral |
| | Cleavage | {100} |
| | Twinning | Cross-hatched-lamellar, two sets {110} |
| | Extinction | |
|
|
| Reaction textures | Breakdown product of plagioclase |
| | Alteration / decomposition | |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | Meta-volcanic rocks in low-grade contact aureoles; ocean-floor basalts affected by ocean-floor metamorphism. Wairakite is indicative of upper zeolite facies conditions. |
| | | Sed | Deep-sea sediments |
| | | Hyd | Precipitate in cavities of rocks from active and fossil geothermal areas |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Pseudocubic habit, twinning
Note: Reliable identification of zeolite species may require chemical analysis, X-ray diffraction, and/or DTA
|
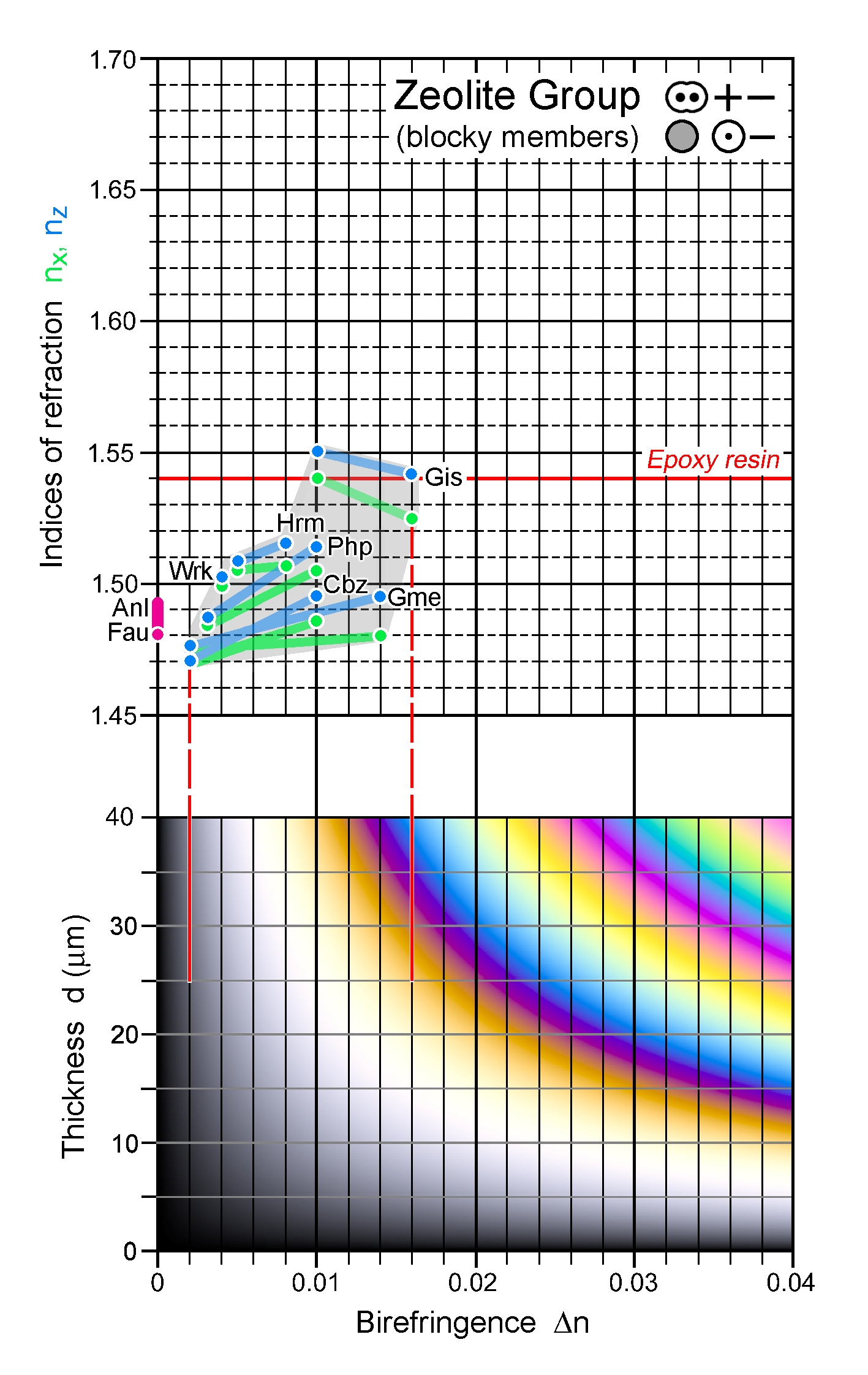
| | Additional comments | Wairakite forms a solid solution with analcime. With decreasing Ca content, its monoclinic character diminishes gradually, and at Ca/(Ca+Na) = 0.33 the monoclinic symmetry is lost.
n-Δn chart: Anl – analcime, Cbz – chabazite, Fau – faujasite, Gis - gismondine,
Gme – gmelinite, Hrm – harmotome, Php – phillipsite, Wrk - wairakite |
|
|

 Images
Images 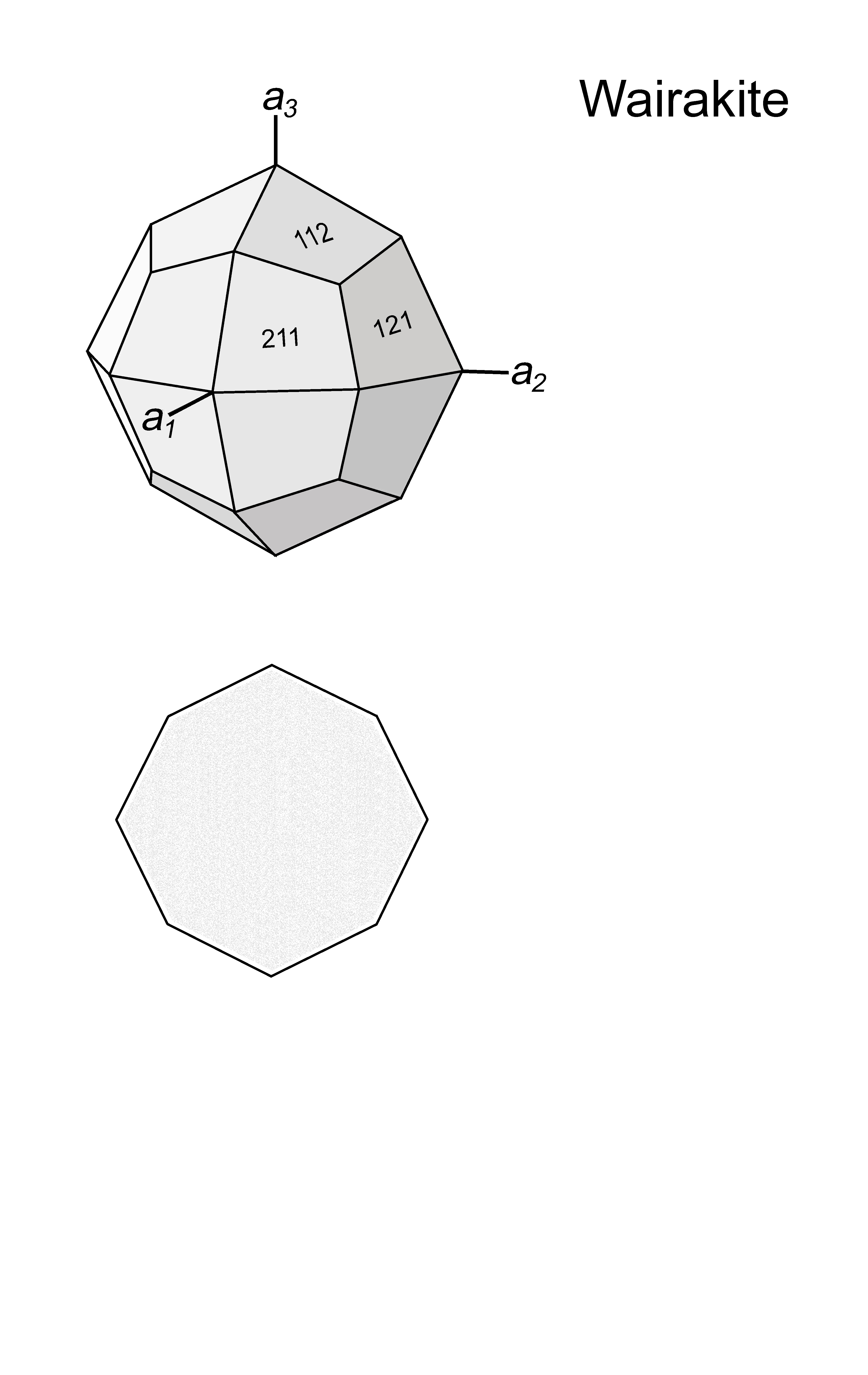

 Images
Images 
