|
| Formula | PbCO3 |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | X = c, Y = b, Z = a |
| | Optical plane | (010) |
| | Relief | High to very high |
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.803
|
|
ny = 2.074
|
|
nz = 2.076
|
|
| 0.273 |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.273 |
| | | |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 9° - |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | Impractical to use due to extreme Δn and highly variable crystal forms |
| | Interference figure | Sections ⊥ c show acute bisectrix figures with very low 2V and numerous isochromes |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | - |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Highly variable; tabular, granular, elongate parallel c or a; pseudohexagonal-dipyramidal, fibrous |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to anhedral |
| | Cleavage | {110} 2 sets; {021} 2 sets |
| | Twinning | {110} contact twins, simple, lamellar, or cyclic forming sixlings; {130} simple contact twins |
| | Extinction | Straight to traces of prism faces and cleavage in sections parallel to c; symmetrical to cleavage in sections orthogonal to c |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | Cerussite is itself a common alteration product of galena |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | Oxidised zone of hydrothermal lead sulfide deposits |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Extreme birefringence with high-order white interference colours; characteristic cleavage, extinction behaviour; biaxial character, twinning; restricted occurrence. Unlike other orthorhombic carbonates, cerussite has no low-relief position in any section. Distinction of cerussite from other carbonates also by staining techniques. |
| | Additional comments | n-Δn chart: Arg - aragonite, Cer - cerussite, Str - strontianite, Wth - witherite |
|
|

 Images
Images 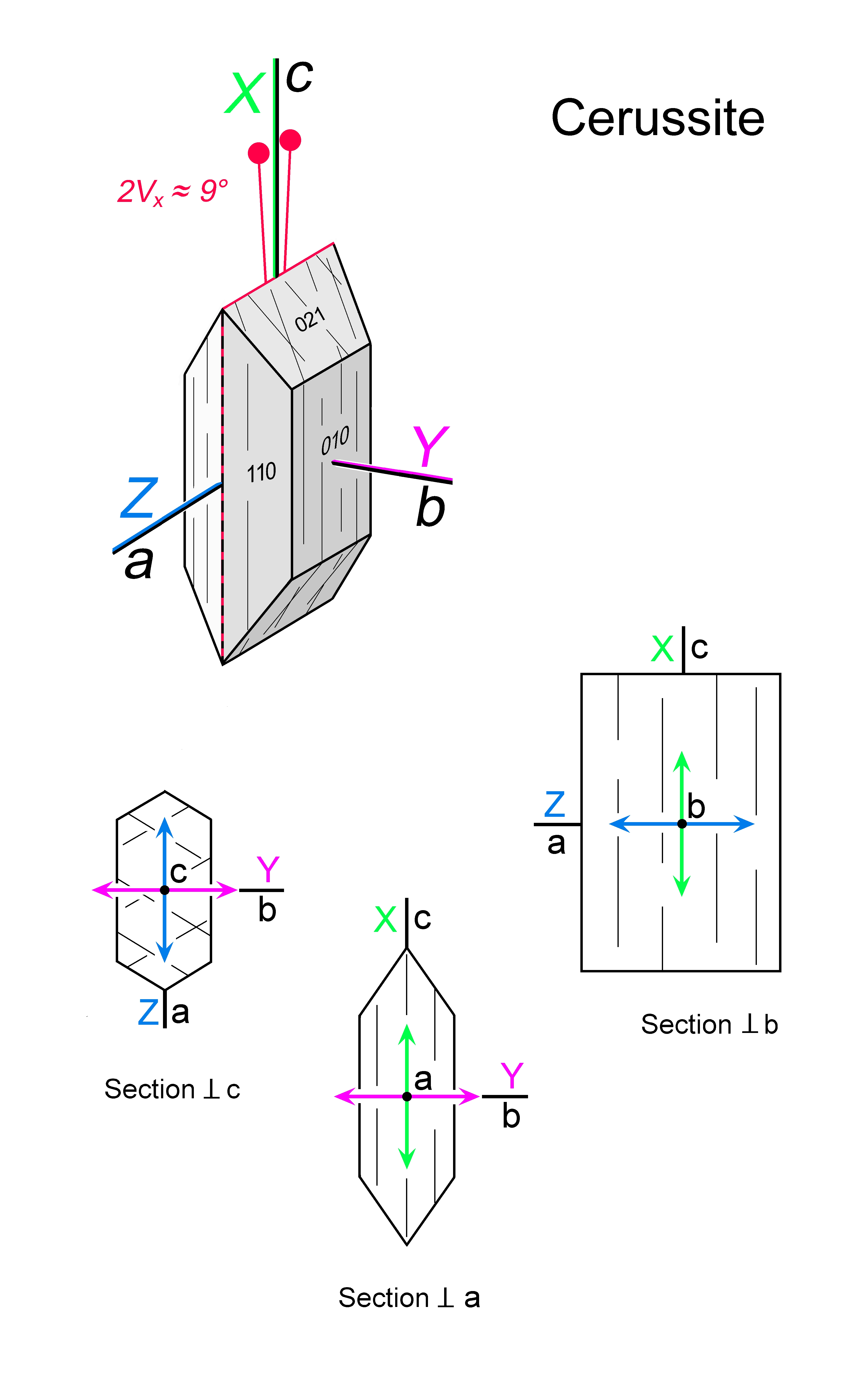


 Images
Images 
