|
| Formula | BaAl2Si2O8 • H2O |
| | Optic class & sign | Biaxial negative |
| | Optical orientation | X = c, Y = a or b, Z = b or a |
| | Optical plane | (100) or (010) |
| | Relief | Moderate-positive |
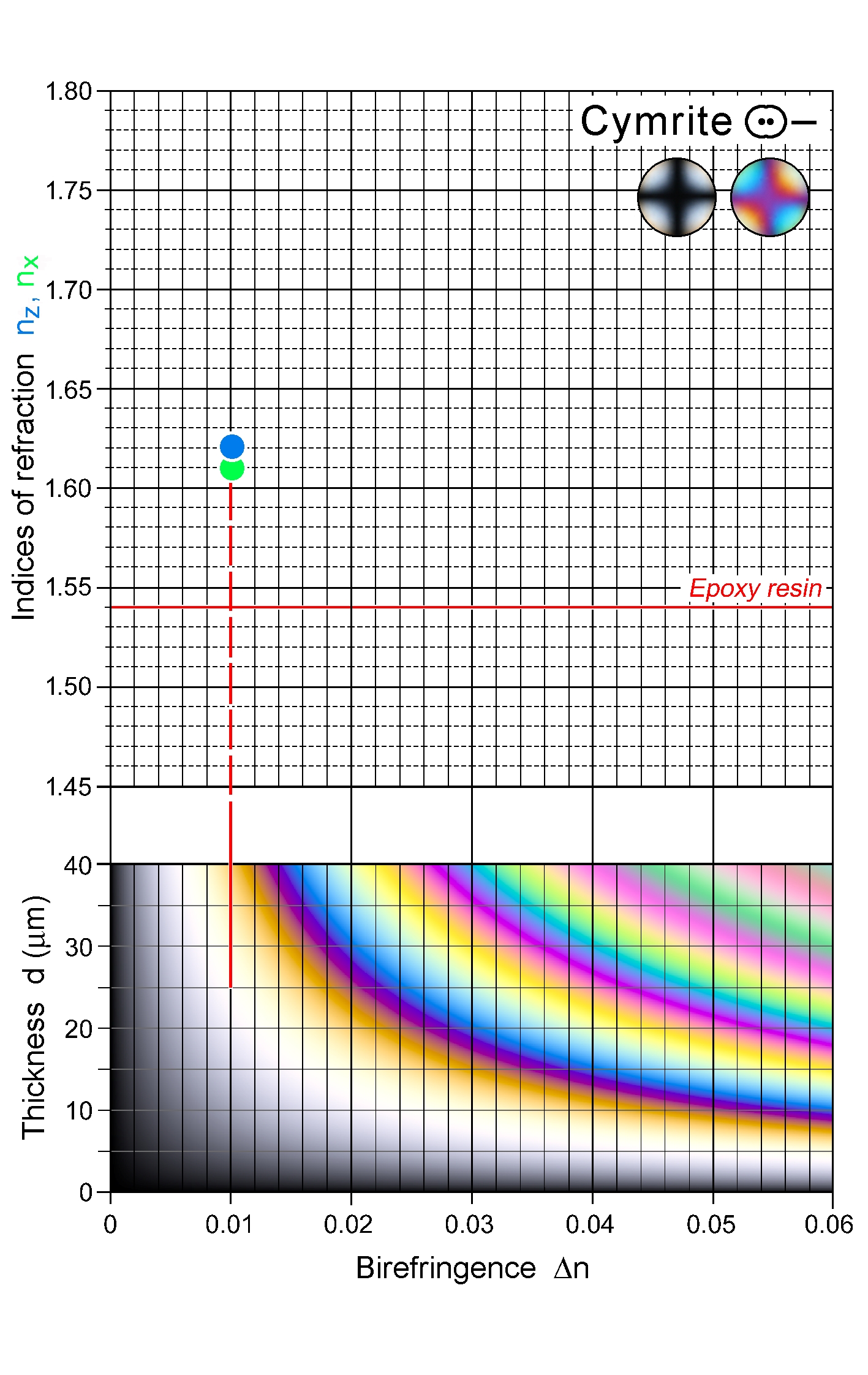
| | Refractive indices | nx = 1.611
|
|
ny = 1.619
|
|
nz = 1.621
|
|
| - |
| | Birefringence (max.) | 0.010 |
| | | - |
| | Optic Angle
| 2Vx
= 0 - 5° |
| | 2Vz
|
| | Sign of elongation | Length-slow, l (+) in sections ∥ c |
| | Interference figure | Pseudo-uniaxial figure; broad isogyre cross, grey to white interference colours |
| | Colour / pleochroism | Colourless |
| | Zoning | - |
|
|
| Form | Habit | Pseudohexagonal platelets or short-prismatic crystals, granular, fibrous |
| | | Surface | Euhedral to subhedral |
| | Cleavage | {001} |
| | Twinning | |
| | Extinction | Essentially straight to traces of prism faces as well as (001) faces and cleavage |
|
|
| Reaction textures | |
| | Alteration / decomposition | |
|
|
| Occurence | Ign | |
| | | Met | High-pressure, low-temperature rocks |
| | | Sed | |
| | | Hyd | Veins in Mn-silicate ore |
| | | Other | |
|
|
| Distinctive properties | Birefringence, relief, crystal form |
| | Additional comments | Pseudohexagonal
The K-equivalent K-cymrite, KAlSi3O8 • H2O (not IMA-approved yet) is stable under ultrahigh pressures only (P>3 GPa). K-cymrite is hexagonal, opt. negative. Its relief is distinctly lower than that of cymrite, with nO = 1.553 and nE = 1.521. |
|
|

 Images
Images 

 Images
Images 
